Your Guide to What Causes Psoriatic Arthritis
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Arthritis FAQ and related What Causes Psoriatic Arthritis topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about What Causes Psoriatic Arthritis topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Arthritis FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Unlocking the Mystery: Understanding the Causes of Psoriatic Arthritis
Imagine waking up with stiff joints and unrelenting pain. If you're living with psoriatic arthritis, this might be part of your reality. Often misunderstood and misdiagnosed, psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic condition affecting millions. This guide delves into what causes this painful ailment, providing insights and understanding around its complexities.
🌿 The Basics: What Is Psoriatic Arthritis?
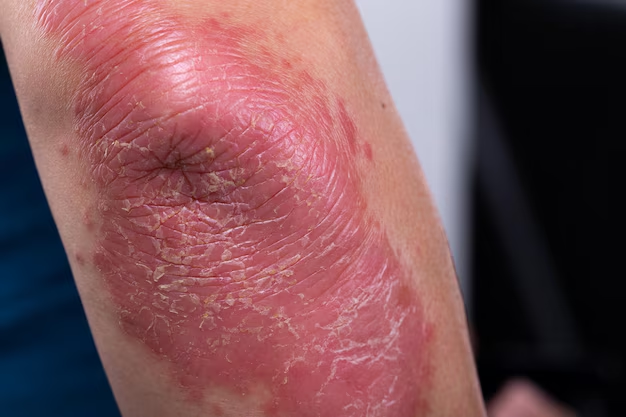
Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory arthritis associated with the skin condition psoriasis. While not every psoriasis patient will develop PsA, around 30% might experience both skin and joint symptoms. The condition leads to swollen, painful joints and can impact any part of the body, including fingertips and spine. Not only can PsA cause physical discomfort, but it can also contribute to fatigue and emotional strain.
Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Close Relationship
At the root, psoriasis is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to red, scaly patches. In PsA, this misguided immune response extends to joint tissues, sparking inflammation and pain. The intertwined nature of these conditions signifies a genetic and environmental tug-of-war that is crucial to understanding PsA.
🔍 Delving Deeper: What Causes Psoriatic Arthritis?
1. Genetic Factors
The genetic link in PsA is notable. Research shows that many PsA patients have a family history of psoriasis or arthritis. Certain genes might increase the risk, with the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) being a significant player. These genes are involved in how the body’s immune system functions, offering clues as to why the body's defenses might turn against its own tissues.
2. Immune System Dysregulation
In psoriatic arthritis, the immune system becomes overly active, attacking not just the skin but joints as well. This misdirected immune activity leads to inflammation — the inflammation responsible for both the skin plaques and joint damage seen in PsA. Learning what triggers such immune dysregulation is key to managing the condition.
3. Environmental Triggers
Beyond genetics and immune factors, environmental triggers also play a substantial role. Key considerations include:
- Infections: Infections might kickstart or worsen PsA symptoms by disrupting normal immune function.
- Injuries: Physical trauma or injury can sometimes precipitate arthritis symptoms in those predisposed to PsA.
- Stress: Chronic stress affects immune responses, potentially exacerbating PsA.
4. Lifestyle and Health Factors
While lifestyle doesn't cause PsA, certain choices can influence symptoms:
- Obesity: Increased body weight puts extra pressure on joints, exacerbating PsA symptoms.
- Smoking and Alcohol Use: Both have been linked to increased severity of symptoms and reduced effectiveness of treatment.
- Diet: An anti-inflammatory diet might help in managing symptoms, although it’s not a direct cause.
🔄 Related Discussions: Exploring Subtopics
🎯 Psoriatic Arthritis vs. Rheumatoid Arthritis
While both PsA and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cause joint pain and swelling, their root causes differ. RA is an autoimmune disorder affecting joint linings, while PsA involves the skin and other tissues in addition to joints. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective management.
🗺️ The Path to Diagnosis
Diagnosing PsA involves a thorough examination, medical history evaluation, and consideration of symptoms. Unlike some conditions, there is no single test to diagnose PsA, meaning healthcare providers rely on a combination of methods to pinpoint the issue.
💡 Managing Psoriatic Arthritis
While there is no cure, various strategies can assist in managing symptoms:
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs, biologics, and DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs) form the mainstay of treatment.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Regular exercise, weight management, and stress reduction techniques can support overall well-being.
- Monitoring & Follow-up: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers ensure that treatment remains effective and adjusted to changing needs.
⏳ The Future of PsA Research
The landscape of PsA research continues to evolve. Scientists are actively exploring new treatments and interventions, striving to provide hope for those grappling with this complex condition. Understanding the molecular and genetic basis of PsA promises a brighter future for patients.
📋 Quick Summary: Key Takeaways on Psoriatic Arthritis
Here's a concise recap with visual appeal:
- 🔬 Genetics & Immune System: PsA is linked to genetic predispositions and immune dysregulation.
- 🌍 Environmental & Lifestyle Triggers: Infections, injuries, and lifestyle factors like obesity and smoking can exacerbate symptoms.
- 🔄 Diagnosis & Management: A multi-faceted approach involving medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring is essential for managing PsA.
- 🔮 Ongoing Research: Future research offers hope for better understanding and treating PsA.
Embed this information into your life to better navigate psoriatic arthritis:
- 🌿 Adopt anti-inflammatory dietary habits.
- 🏋️♀️ Engage in regular, suitable exercise.
- 🚭 Reconsider smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- 📅 Schedule regular healthcare check-ups for tailored care.
Understanding PsA fully encompasses appreciating its roots in genetic, immune, environmental, and lifestyle factors. While psoriatic arthritis remains a challenging condition, insights into its causes offer a path to more effective management and a better quality of life. Continual learning and adapting to new scientific discoveries is a beacon of hope for those affected.
What You Get:
Free Arthritis FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about What Causes Psoriatic Arthritis and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about What Causes Psoriatic Arthritis topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Arthritis FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Septic Arthritis
- Are Bananas Bad For Arthritis
- Are Tomatoes Bad For Arthritis
- Can An Inflamed Nerve Cause Arthritis
- Can An Inflamed Nerve Cause Arthritis In Dogs
- Can An x Ray Show Arthritis
- Can Arthritis Be Cured
- Can Arthritis Be Reversed
- Can Arthritis Become Septic After Infection From Injection
- Can Arthritis Cause Numbness
