Your Guide to Can You Die From Gout Arthritis
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Arthritis FAQ and related Can You Die From Gout Arthritis topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about Can You Die From Gout Arthritis topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Arthritis FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Is Gout Arthritis Life-Threatening? Understanding the Risks and Realities
Gout, a form of arthritis characterized by severe pain, redness, and tenderness in joints, has long been a topic of concern for many. While it is well understood as a painful condition, a pressing question is: Can gout be fatal? Let's explore this question from multiple angles to provide you with a clear understanding of the relationship between gout arthritis and overall health risk.
What Is Gout, and Why Does It Occur?
Understanding the Causes
Gout arises from an accumulation of uric acid crystals in your joints, a condition fueled by high levels of uric acid in the blood. Various factors can contribute to this build-up:
- Diet: High purine foods, like red meat and seafood, can increase uric acid levels.
- Lifestyle: Alcohol consumption and obesity are known contributors.
- Genetics: Family history can play a significant role in your predisposition.
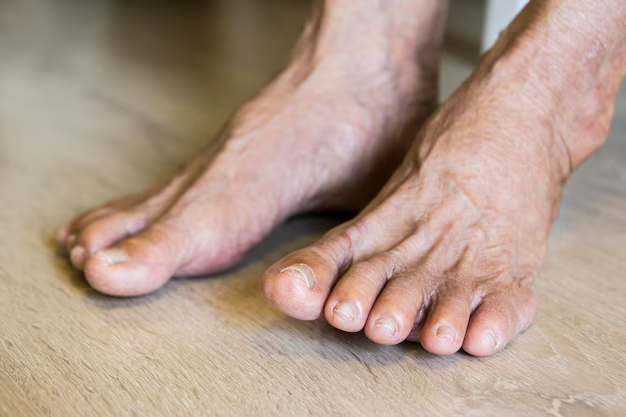
Symptoms to Watch
Symptoms typically appear suddenly, often manifesting at night, and include:
- Intense joint pain, particularly in the big toe.
- Lingering discomfort even after severe pain dissipates.
- Inflammation and redness in the affected areas.
Understanding these symptoms can help in managing and anticipating flare-ups, but can it lead to greater health problems?
The Direct Risks Associated with Gout
Does Gout Itself Cause Death?
Gout is not directly fatal. However, if left untreated, it can lead to complications that increase health risks:
- Tophi Formation: Chronic gout can lead to the development of tophi, nodules which can damage bones and joints.
- Joint Damage: Prolonged inflammation may cause permanent damage to joints, leading to disability.
Indirect Health Risks
More concerning is the relationship between gout and other serious health conditions that could potentially be life-threatening:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Individuals with gout often face higher risks of heart disease and hypertension.
- Kidney Problems: High uric acid levels stress the kidneys, potentially resulting in kidney stones or even kidney failure.
Exploring these connections with a healthcare professional is crucial for managing overall health effectively.
Managing Gout: Practical Steps for Prevention
Lifestyle Adjustments
Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks:
- Diet: Focus on low-purine foods—opt for fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated helps flush uric acid from the body.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reducing weight can decrease uric acid levels and reduce joint stress.
Medical Management
Prescribed medications can help manage gout more effectively:
- Uric Acid Lowering Agents: These medications help reduce uric acid production.
- Anti-Inflammatories: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can alleviate pain during attacks.
Before embarking on any treatment strategy, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to tailor approaches for individual needs.
Related Health Factors: Cardiovascular and Renal Concerns
Heart Health Implications
The link between gout and cardiovascular conditions is discussed broadly in medical circles:
- Individuals with gout often exhibit risk factors like high blood pressure, which, if unmanaged, can contribute to heart diseases.
Renal Function
Kidney health is another area closely tied to gout:
- Chronic high uric acid levels can damage renal tissues and impair kidney functionality over time.
These connections emphasize the importance of holistic management of gout, considering its broader health impacts.
Key Takeaways and Practical Insights
To succinctly summarize how gout might impact your health and practical steps towards managing it, consider the following bullet points:
🧩 Gout Itself Isn't Fatal: The danger lies in complications and other related conditions.
🥦 Diet and Lifestyle Matter: Focus on a low-purine diet and regular exercise.
💊 Medication Is Key: Effective management includes the use of proper medications in consultation with healthcare providers.
❤️ Monitor Related Health Issues: Be proactive about cardiovascular and kidney health to reduce overall risk.
Looking Ahead: Proactive Health Management
Understanding and managing gout through diet, lifestyle changes, and medical intervention can significantly reduce the risks associated with this condition. By keeping a vigilant eye on related health factors such as cardiovascular and renal health, you can minimize potential complications. Remember, while gout itself isn’t directly life-threatening, the ripple effects it can have on other health conditions warrant serious consideration. Stay informed, stay proactive, and consult healthcare professionals regularly to navigate your health journey effectively.
What You Get:
Free Arthritis FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about Can You Die From Gout Arthritis and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about Can You Die From Gout Arthritis topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Arthritis FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Septic Arthritis
- Are Bananas Bad For Arthritis
- Are Tomatoes Bad For Arthritis
- Can An Inflamed Nerve Cause Arthritis
- Can An Inflamed Nerve Cause Arthritis In Dogs
- Can An x Ray Show Arthritis
- Can Arthritis Be Cured
- Can Arthritis Be Reversed
- Can Arthritis Become Septic After Infection From Injection
- Can Arthritis Cause Numbness
