Your Guide to Can x Rays Detect Arthritis
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Arthritis FAQ and related Can x Rays Detect Arthritis topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about Can x Rays Detect Arthritis topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Arthritis FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Detecting Arthritis with X-Rays: What You Need to Know
Arthritis, a condition characterized by inflammation and stiffness of the joints, is a word that often leads to concerns about pain and mobility. With millions affected worldwide, the ability to diagnose arthritis swiftly and accurately is a pressing need for healthcare professionals and patients alike. But can X-rays truly detect arthritis, and if so, to what extent? Let’s delve into how effective X-rays are in diagnosing arthritis and explore alternative diagnostic tools that complement them in the diagnosis process.
🔍 Understanding Arthritis: A Quick Overview
Types of Arthritis: Arthritis isn't a single disease; it includes over 100 different types, with osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) being the most common. OA is typically caused by wear and tear, while RA is an autoimmune condition leading to joint inflammation.
Symptoms and Progression: Common symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. The severity and progression vary widely among individuals.
Importance of Early Detection: Early diagnosis can be crucial in managing symptoms and slowing the disease's progression. Identifying the type of arthritis allows for more tailored treatment approaches.
🩻 The Role of X-Rays in Detecting Arthritis
How X-Rays Work
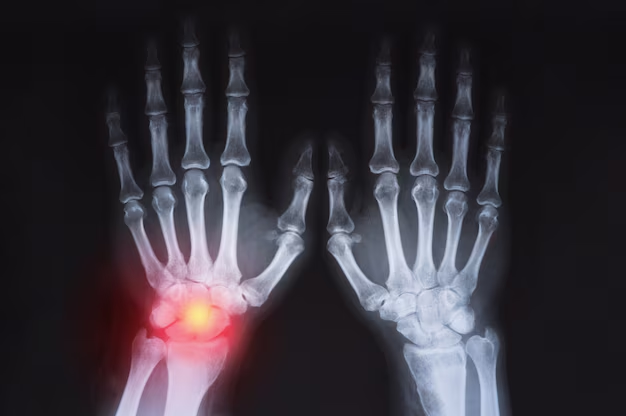
X-rays, a form of electromagnetic radiation, pass through the body to create images of tissues and structures. They’re particularly useful for visualizing bones and can show changes in joint structures that indicate arthritis.
What X-Rays Reveal
Osteoarthritis Indicators: X-rays can show joint space narrowing, bone spurs, and changes in bone shape, which are indicative of OA. These images are crucial for confirming a diagnosis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Markers: In RA, X-rays may reveal joint erosion and changes in joint alignment over time. However, early RA may not show noticeable changes on an X-ray, necessitating additional tests.
Limitations of X-Rays
While X-rays are a valuable diagnostic tool due to their ability to reveal bone changes and joint damage, they do have limitations:
Soft Tissue Imaging: X-rays aren’t as effective in displaying soft tissues like cartilage, tendons, and ligaments, which can be involved in arthritis.
Early Detection: Subtle early signs of inflammation, especially in RA, might not be visible. Changes may only become apparent after significant damage has occurred.
🔬 Beyond X-Rays: Complementary Diagnostic Tools
To achieve a comprehensive diagnosis, healthcare providers often utilize a combination of diagnostic methods alongside X-rays:
1. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Advantages: MRI provides detailed images of both bone and soft tissue, making it ideal for detecting early arthritis changes not visible on X-rays.
- Use in Arthritis: Particularly useful in spotting early RA changes and assessing soft tissue damage, MRI serves well in monitoring disease progression and treatment efficacy.
2. Ultrasound
- Advantages: Offers real-time imaging of joint inflammation and fluid accumulation.
- Use in Arthritis: Ultrasound is a preferred method for evaluating RA due to its ability to detect early inflammatory changes and guide needle placement during joint aspirations.
3. Blood Tests
- Purpose: Often employed to identify specific markers of inflammation and autoantibodies.
- Common Markers: Tests like ESR, CRP levels, and rheumatoid factor provide supplementary data that aid the diagnostic process, especially for autoimmune arthritis types like RA.
📋 Key Takeaways for Detecting Arthritis with Imaging
Here's a quick summary of what you need to keep in mind:
- 🔍 X-rays are helpful for viewing bone changes in osteoarthritis and late-stage rheumatoid arthritis.
- 🦴 MRI and Ultrasound are essential for early detection and for viewing soft tissues and inflammatory markers.
- 📊 Blood Tests complement imaging by identifying inflammation and specific arthritis types.
- 🚫 Limitations: X-rays alone may not detect early-stage arthritis or soft tissue changes adequately.
🤔 Deciding on Diagnosis: The Expert Approach
When symptoms suggest arthritis, healthcare professionals consider several factors before prescribing diagnostic tests:
Symptom History: Detailed patient history can guide the choice of initial imaging or tests to perform.
Type of Suspected Arthritis: Depending on whether OA or RA is suspected, different imaging choices may be prioritized.
Options and Recommendations: MRI might be recommended if a clearer picture of early joint changes is necessary, while blood tests might be used for more definitive RA diagnosis.
🧠 Understanding the Diagnostic Journey
For anyone navigating the often-complex journey to an arthritis diagnosis, it’s important to understand that:
- Diagnosis is Multifaceted: No single test rules in or out arthritis; a combination approach often provides a clearer picture.
- Patient Involvement is Key: Open communication with healthcare providers ensures all symptoms are expressed and options are fully considered.
- Technology is Continuously Evolving: Understanding the strengths and limitations of each diagnostic tool empowers informed decisions about care and diagnosis.
🌈 Making the Most of Your Consultations
When visiting a healthcare provider regarding potential arthritis, consider how you can make the most of your consultation:
Prepare to Discuss Symptoms: Note down symptom history, severity, and any patterns discerned over time.
Ask About Various Test Options: Don’t hesitate to inquire why a specific test is being recommended and ask about the different imaging technologies available.
Follow Through with Recommended Follow-up: Understanding that diagnosis may require multiple visits and tests helps manage expectations and stress.
🔄 Managing Expectations: From Diagnosis to Treatment
- Diagnosis can be a Process: It often involves several steps and expert interpretations across multiple modalities.
- Treatment Plans: After diagnosis, treatment plans are personalized based on severity, type of arthritis, and lifestyle factors.
As diagnostic technologies advance, so does the ability to detect arthritis earlier and with greater accuracy. Each method, whether a traditional X-ray or a cutting-edge MRI, carries its unique strengths and plays a crucial role in the comprehensive approach to understanding and managing arthritis effectively. While X-rays remain a cornerstone in diagnostic imaging, integrating them with other methods offers the most robust pathway to diagnosis and ongoing management.
What You Get:
Free Arthritis FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about Can x Rays Detect Arthritis and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about Can x Rays Detect Arthritis topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Arthritis FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Septic Arthritis
- Are Bananas Bad For Arthritis
- Are Tomatoes Bad For Arthritis
- Can An Inflamed Nerve Cause Arthritis
- Can An Inflamed Nerve Cause Arthritis In Dogs
- Can An x Ray Show Arthritis
- Can Arthritis Be Cured
- Can Arthritis Be Reversed
- Can Arthritis Become Septic After Infection From Injection
- Can Arthritis Cause Numbness
