Your Guide to What Reading Is Hypertension
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about HyperTension FAQ and related What Reading Is Hypertension topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about What Reading Is Hypertension topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to HyperTension FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Understanding Hypertension: The Numbers You Should Know
Imagine visiting your doctor for a routine check-up and hearing the term "hypertension" during the conversation. You might wonder, “What does it mean, and why is it important?" Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a condition that affects millions globally, often sneaking up without noticeable symptoms but potentially leading to severe health issues if left unchecked. Understanding the blood pressure readings that signify hypertension is crucial for maintaining health and preventing complications.
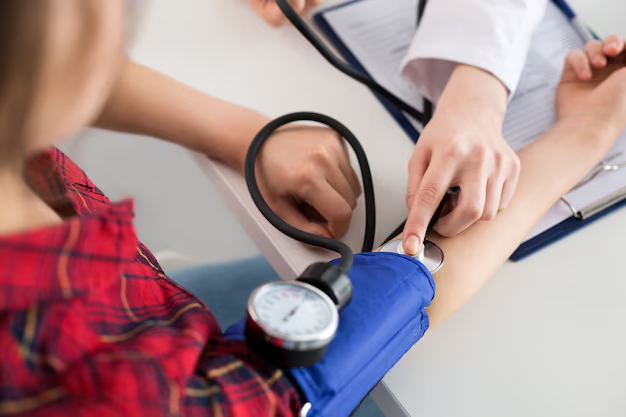
Blood Pressure Basics
Blood pressure measures the force of blood pushing against the walls of your arteries. It's recorded in two numbers: systolic pressure (the top number) and diastolic pressure (the bottom number).
- Systolic pressure represents the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats.
- Diastolic pressure indicates the pressure in the arteries when your heart rests between beats.
Hypertension Numbers
According to health authorities like the American Heart Association, hypertension is diagnosed when your blood pressure readings reach or exceed 130/80 mmHg consistently. The condition is categorized into different stages:
- Elevated: Systolic between 120-129 and diastolic less than 80.
- Stage 1 Hypertension: Systolic between 130-139 or diastolic between 80-89.
- Stage 2 Hypertension: Systolic at least 140 or diastolic at least 90.
- Hypertensive Crisis: Systolic over 180 and/or diastolic over 120; immediate medical attention is needed.
Why Monitor Blood Pressure?
Hypertension is notorious for being a "silent killer" because it can damage your heart, kidneys, and brain without causing obvious symptoms. Regular monitoring is crucial, particularly if you have risk factors such as obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, high salt intake, excessive alcohol consumption, or a family history of high blood pressure.
Taking Control of Hypertension
Managing your blood pressure can seem daunting, but it's achievable through lifestyle changes such as:
- Adopting a balanced diet, rich in vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
- Engaging in regular physical activity to maintain a healthy weight.
- Reducing salt intake and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
- Quitting smoking to improve overall cardiovascular health.
- Monitoring your blood pressure at home and having regular check-ups.
Financial and Educational Resources
Managing hypertension can sometimes involve unforeseen costs, such as medication, regular doctor visits, or specialized diets. Fortunately, several financial aid programs and educational opportunities can help ease the burden:
- Government Aid Programs: Check if you qualify for Medicaid or Medicare to help cover medical expenses related to hypertension.
- Financial Assistance for Medications: Programs like the Pharmaceutical Assistance Program offer discounts or free medications.
- Debt Relief Options: If medical bills are piling up, consider seeking assistance from organizations that specialize in healthcare-related debt relief.
- Educational Grants: Consider enrolling in community health workshops often funded through educational grants to learn more about managing hypertension effectively.
- Credit Card Solutions: Some credit cards offer health care financing plans with lower interest rates, making it easier to manage medical expenses.
🔍 Key Resources for Hypertension Management:
- 🏥 Medicaid/Medicare: Health care coverage options
- 💊 Pharmaceutical Assistance Programs: Reduced-cost medications
- 📚 Health Workshops: Community education and support
- 💳 Healthcare Credit Options: Lower interest financial plans for medical bills
- 🌟 Non-Profit Organizations: Support for managing healthcare expenses
Taking proactive steps to understand and manage hypertension not only safeguards your health but also helps you plan and prepare for potential financial implications. By leveraging available resources, you can ensure that both your physical and financial health are well-maintained.
What You Get:
Free HyperTension FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about What Reading Is Hypertension and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about What Reading Is Hypertension topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to HyperTension FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a 66 Year Old Female With a History Of Hypertension
- Are Eggs Bad For Hypertension
- Are Eggs Good For Hypertension
- Are Endocrine Disorders Causing Hypertension Rare
- Can Adderall Cause Hypertension
- Can Alcohol Cause Hypertension
- Can Allergies Cause Hypertension
- Can Anemci People Get Hypertension
- Can Anemia Cause Hypertension
- Can Antibiotics Cause Hypertension
