Your Guide to How To Help Hypertension
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about HyperTension FAQ and related How To Help Hypertension topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about How To Help Hypertension topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to HyperTension FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Simple Strategies for Managing Hypertension at Home
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is more than just a common ailment—it’s a silent health risk that can lead to serious complications like heart disease and stroke if left unmanaged. Understanding how to help hypertension naturally and effectively can significantly enhance your well-being and longevity.
Embrace Heart-Healthy Nutrition
Adopting a balanced diet is one of the most impactful lifestyle changes you can make. Focus on incorporating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your meals. The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is a proven method that emphasizes reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium, calcium, and magnesium, which are crucial in lowering blood pressure.
Stay Active
Regular physical activity is not just a recommendation—it’s a necessity for those looking to manage hypertension. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, each week can help lower your blood pressure over time. Exercise also has the bonus of reducing stress, enhancing mood, and supporting weight management.
Keep a Check on Stress Levels
Managing stress is vital in handling high blood pressure. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga can be effective in helping you keep calm. These practices reduce stress hormones that can elevate blood pressure, contributing to overall health improvement.
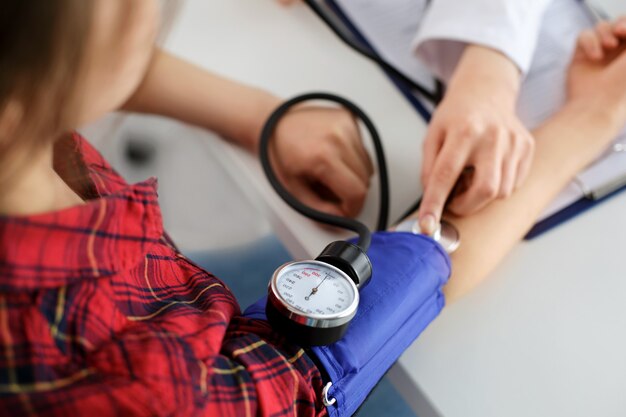
Measure Your Blood Pressure Regularly
Investing in a home blood pressure monitor allows you to track your levels and observe what lifestyle changes are most effective for you. Keeping a log of your daily readings will help you and your healthcare provider better understand your health trends and tailor more specific recommendations.
Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking
Consuming alcohol in moderation and stopping smoking can have significant impacts on blood pressure control. Excessive drinking can raise blood pressure to unhealthy levels, and smoking damages blood vessels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular conditions.
Explore Financial Assistance Programs
The journey to better health isn’t always straightforward, especially if financial stress is a concern. Government aid programs can offer substantial support. Options like Medicaid and Medicare assist with healthcare costs, providing you access to necessary treatments and medications.
Additionally, if you're burdened by medical bills, various debt relief options and credit card solutions can help manage these expenses without compromising your care. Look into organizations that offer credit counseling or tailor-made solutions for those impacted by high medical costs.
Educational Resources and Opportunities
If you’re interested in furthering your knowledge and skills in managing hypertension, consider pursuing educational grants that can fund courses in nutrition, health coaching, or any related field. These enhanced skill sets can empower you to make informed health decisions.
By prioritizing practical lifestyle changes and exploring available financial and educational resources, you can successfully manage hypertension and improve your overall quality of life.
Here’s a quick look at resourceful options that could support your health journey:
- 💰 Government Aid Programs: Explore Medicaid and Medicare for healthcare assistance.
- 📉 Debt Relief and Credit Solutions: Check for credit counseling and tailored debt management programs.
- 🎓 Educational Grants: Look for grants supporting further learning in health and nutrition fields.
- 🚴♀️ Community Exercise Groups: Join local exercise classes or walking groups for physical and social engagement.
- 🍏 Healthy Eating Workshops: Find workshops or seminars promoting healthy eating habits.
Taking advantage of these tools and strategies can pave the way to a healthier, more balanced lifestyle. Dive into these solutions today to gain control over hypertension while ensuring financial peace of mind.
What You Get:
Free HyperTension FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about How To Help Hypertension and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about How To Help Hypertension topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to HyperTension FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a 66 Year Old Female With a History Of Hypertension
- Are Eggs Bad For Hypertension
- Are Eggs Good For Hypertension
- Are Endocrine Disorders Causing Hypertension Rare
- Can Adderall Cause Hypertension
- Can Alcohol Cause Hypertension
- Can Allergies Cause Hypertension
- Can Anemci People Get Hypertension
- Can Anemia Cause Hypertension
- Can Antibiotics Cause Hypertension
