Your Guide to How To Diagnose Pulmonary Hypertension
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about HyperTension FAQ and related How To Diagnose Pulmonary Hypertension topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about How To Diagnose Pulmonary Hypertension topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to HyperTension FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Understanding Pulmonary Hypertension: Steps to Diagnosis
When it comes to diagnosing pulmonary hypertension (PH), early detection is crucial for effective management. Pulmonary hypertension is a condition characterized by elevated blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs, which can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. Here’s a straightforward guide to help you understand the diagnostic journey.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Before any medical tests, recognizing early symptoms can prompt timely diagnosis. Symptoms of pulmonary hypertension often include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or fainting spells
- Swelling in the ankles, legs, and abdomen
- Chest pain
If you experience any of these signs, it's important to consult a healthcare provider who can initiate diagnostic steps.
Initial Assessment and Tests
The Importance of Medical History and Physical Examination
Your doctor will start by taking a thorough medical history and performing a physical examination. This will help rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An ECG records the electrical activity of your heart and can reveal signs of strain on the right side of the heart, indicative of pulmonary hypertension.
Echocardiogram
Often considered the frontline test, an echocardiogram uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart, allowing your doctor to assess the heart’s structure and monitor blood flow.
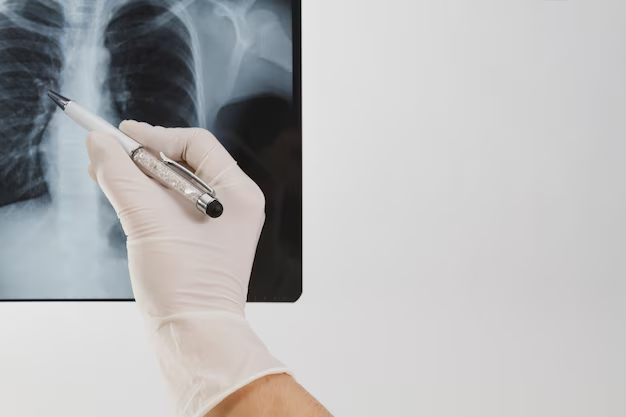
Chest X-ray
A chest X-ray can identify characteristic changes in the lungs and heart, such as enlargement of arteries which suggests pulmonary hypertension.
Pulmonary Function Tests
These tests evaluate how well your lungs are working and can help to distinguish pulmonary hypertension from other lung-related conditions.
Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
Right Heart Catheterization
For a definitive diagnosis, a right heart catheterization is often performed. This procedure measures the blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries and is critical to confirming pulmonary hypertension.
Additional Tests
If the cause of pulmonary hypertension remains unclear, further tests may include:
- CT or MRI scans: To provide detailed images of the blood vessels.
- Blood tests: To identify underlying conditions.
- Ventilation/Perfusion (V/Q) scan: To check for blood clots in the lungs.
Exploring Health and Financial Resources
While the journey of diagnosing and treating pulmonary hypertension can be demanding, there are resources available to ease the burden. Here are some pathways to explore for support:
- Government Aid Programs: Assistance may be available through programs like Medicaid, which can help cover medical costs for eligible individuals.
- Financial Assistance: Non-profit organizations often provide grants or financial aid for those with chronic conditions.
- Debt Relief Options: Consider consulting with a financial advisor to explore debt consolidation or relief programs if medical expenses are overwhelming.
- Credit Card Solutions: Some credit card companies offer hardship programs for those facing financial challenges due to medical conditions.
- Educational Grants: These can be invaluable for patients seeking further education or vocational training due to a change in career capacity resulting from their condition.
No one should face pulmonary hypertension alone. Understanding your diagnosis is the first step towards managing the condition effectively and improving your quality of life.
Financial and Educational Support Options 📑
- Medicaid & Medicare: Health coverage for low-income individuals or those over 65.
- Patient Assistance Programs: Offered by pharmaceutical companies for medication costs.
- Debt Management Plans (DMPs): Through nonprofit credit counseling agencies.
- Hardship Programs: Offered by various banks and lenders for temporary relief.
- Scholarships for Medical Conditions: Financial support for education or retraining.
What You Get:
Free HyperTension FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about How To Diagnose Pulmonary Hypertension and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about How To Diagnose Pulmonary Hypertension topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to HyperTension FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a 66 Year Old Female With a History Of Hypertension
- Are Eggs Bad For Hypertension
- Are Eggs Good For Hypertension
- Are Endocrine Disorders Causing Hypertension Rare
- Can Adderall Cause Hypertension
- Can Alcohol Cause Hypertension
- Can Allergies Cause Hypertension
- Can Anemci People Get Hypertension
- Can Anemia Cause Hypertension
- Can Antibiotics Cause Hypertension
