Your Guide to How To Diagnose Hypertension
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about HyperTension FAQ and related How To Diagnose Hypertension topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about How To Diagnose Hypertension topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to HyperTension FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Discovering the Basics of Diagnosing Hypertension
Diagnosing hypertension isn't just a matter of feeling your heartbeat racing or experiencing a sudden headache. It's a more defined process that requires careful monitoring and evaluation. With hypertension affecting millions globally, knowing how to properly diagnose it is key to finding a path toward better health.
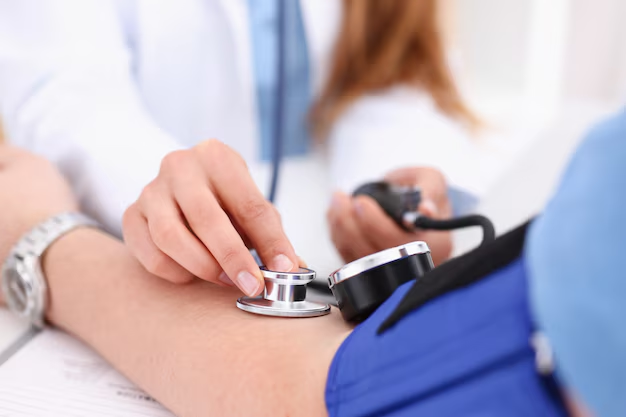
Understanding Blood Pressure Measurements
The cornerstone of diagnosing hypertension lies in understanding blood pressure readings. Blood pressure is recorded using two numbers. The systolic blood pressure (the top number) measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats. Meanwhile, the diastolic pressure (the bottom number) calculates the pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats.
- Normal range: A systolic reading of less than 120 and a diastolic reading of less than 80.
- Elevated blood pressure: Systolic between 120-129 and diastolic less than 80.
- Hypertension Stage 1: Systolic 130-139 or diastolic 80-89.
- Hypertension Stage 2: Systolic at least 140 or diastolic at least 90.
- Hypertensive crisis: Systolic over 180 and/or diastolic over 120, a situation that requires immediate medical attention.
The Role of Regular Monitoring
A single high reading isn't enough for a hypertension diagnosis because blood pressure can fluctuate throughout the day due to a variety of factors. Regular monitoring is vital. Your medical provider might ask you to record your blood pressure at home or use a 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitor to gather comprehensive data.
Medical Assessment & Testing
A comprehensive medical assessment is crucial for diagnosing hypertension. This can involve:
- Blood tests: To check for conditions like cholesterol and diabetes that can contribute to hypertension.
- Urinalysis: To search for signs of kidney disease.
- Electrocardiogram (EKG): To check for heart related issues.
- Additional tests: Such as an echocardiogram, if early signs of heart disease are suspected.
Lifestyle Evaluation
Doctors also consider lifestyle factors when diagnosing hypertension. Factors include diet, physical activity levels, alcohol consumption, and smoking habits. Adjusting these can significantly impact blood pressure levels.
Why Early Diagnosis Matters
Identifying hypertension early is essential. It can prevent severe health complications like heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. Regular health check-ups and blood pressure monitoring are crucial steps in managing your heart health.
Exploring Financial Assistance for Health Management
Dealing with a diagnosis like hypertension often leads to concerns about the associated financial implications. Fortunately, there are many resources available to ease the burden.
- 💰 Government Programs: Medicaid and Medicare offer healthcare assistance, possibly covering the cost of hypertension management and medication.
- 📈 Insurance Plans: Many insurance companies cover routine blood pressure checks and essential hypertension treatments without high out-of-pocket costs.
- 🏥 Community Clinics: Look for local clinics providing services on a sliding scale based on income, often subsidized by government grants.
- 💸 Debt Relief Options: If medical debts are accumulating, exploring debt relief programs can help manage and potentially reduce these balances.
- 🎓 Educational Grants: For students, college health funds and grants can offer support in accessing necessary medical care.
- 💳 Credit Solutions: Consider low-interest personal loans or credit cards dedicated to medical expenses to spread costs over time.
Awareness and proper diagnosis of hypertension can open doors to comprehensive management strategies, ensuring you tackle health challenges while tapping into financial resources for peace of mind.
What You Get:
Free HyperTension FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about How To Diagnose Hypertension and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about How To Diagnose Hypertension topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to HyperTension FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a 66 Year Old Female With a History Of Hypertension
- Are Eggs Bad For Hypertension
- Are Eggs Good For Hypertension
- Are Endocrine Disorders Causing Hypertension Rare
- Can Adderall Cause Hypertension
- Can Alcohol Cause Hypertension
- Can Allergies Cause Hypertension
- Can Anemci People Get Hypertension
- Can Anemia Cause Hypertension
- Can Antibiotics Cause Hypertension
