Your Guide to How To Test For Osteoporosis
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Osteoporosis FAQ and related How To Test For Osteoporosis topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about How To Test For Osteoporosis topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Osteoporosis FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Uncovering the Secrets of Bone Health: How to Test for Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis can sneak up on even the healthiest individuals, turning what seems like a minor fall into a significant health concern. So, it's essential to understand how to test for osteoporosis to safeguard your future well-being. Fortunately, there are effective ways to detect bone density issues early, enabling you to take proactive measures.
Understanding Osteoporosis Testing
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. Often, it goes undetected until after a fracture has occurred, making testing critical for prevention and early intervention. Here are the primary methods used for diagnosing osteoporosis:
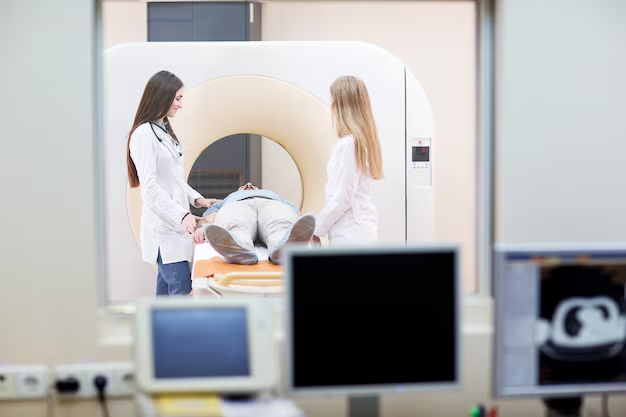
1. Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) Scan
The DEXA scan is the gold standard for osteoporosis testing. It’s a specialized X-ray that measures bone density at the hip and spine. The process is quick, painless, and non-invasive, allowing for accurate assessment of bone health.
- Procedure Length: 15-30 minutes
- Radiation Exposure: Minimal, comparable to natural background radiation
2. Quantitative Ultrasound
Although not as detailed as a DEXA scan, quantitative ultrasound is a convenient alternative. It measures bone density at the heel and can be done in different settings, such as health fairs or mobile testing units.
- Pros: Portable, doesn’t require specialized healthcare settings
- Cons: Less accurate compared to DEXA scans
3. Blood and Urine Tests
While not directly measuring bone density, blood and urine tests can assess markers related to bone turnover. These tests can provide insights into the metabolic activity affecting your bones.
- Role: Complements DEXA/ultrasound by evaluating bone metabolism
When to Test for Osteoporosis
Bone density testing is generally recommended for:
- Women aged 65 and older
- Men aged 70 and older
- Postmenopausal women and men above 50 if they have risk factors, such as a family history of osteoporosis or previous bone fractures
Access to Testing and Financial Support
Navigating the healthcare landscape can be daunting, especially when financial constraints are involved. Luckily, various programs and resources can help ease this burden and ensure that bone health testing is accessible to everyone.
Medicare and Insurance Coverage
For those eligible, Medicare Part B covers bone density tests once every 24 months if you meet certain risk criteria. Many insurance plans also cover osteoporosis testing, particularly for those in high-risk categories.
Government Assistance Programs
Programs such as the Medicaid vary by state but can also cover osteoporosis testing for eligible low-income individuals. Check your state's offerings to understand your coverage options.
Community Health Initiatives
Look out for community health events that offer free or low-cost testing. Many local organizations and hospitals run such events annually.
Stepping into Financial Well-being
Maintaining your bone health is crucial, but so is addressing financial wellness. Consider exploring these resources that can offer support beyond healthcare:
🏥 State Health Programs: Provide reduced-cost testing for those without insurance.
💳 Credit Counseling Services: Help manage medical debt and improve financial literacy.
🎓 Educational Grants: Offer opportunities for further education in health management.
📉 Debt Relief Options: Tailored solutions for reducing existing debt burdens.
Protecting your bone health goes hand in hand with protecting your financial health. Stay informed, stay proactive, and make use of the wide array of resources at your disposal to lead a healthier, happier life.
What You Get:
Free Osteoporosis FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about How To Test For Osteoporosis and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about How To Test For Osteoporosis topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Osteoporosis FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Nurse Is Caring For a Client Who Has Osteoporosis.
- a Percutaneous Is Performed To Treat Osteoporosis Related Compression Fractures
- Can Alcohol Cause Osteoporosis
- Can I Do Pilates If I Have Osteoporosis
- Can I Reverse Osteoporosis
- Can Men Get Osteoporosis
- Can Osteoporosis Affect Teeth
- Can Osteoporosis Be Cured
- Can Osteoporosis Be Painful
- Can Osteoporosis Be Reversed
