Your Guide to How Is Osteoporosis Diagnosed
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Osteoporosis FAQ and related How Is Osteoporosis Diagnosed topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about How Is Osteoporosis Diagnosed topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Osteoporosis FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Discover the Key to Diagnosing Osteoporosis
As we gracefully age, ensuring our bones remain strong and healthy becomes increasingly important. Osteoporosis, often dubbed the "silent disease," can cause bones to become fragile and more susceptible to fractures. But how exactly is osteoporosis diagnosed, and what steps can you take if you find yourself or a loved one facing this condition?
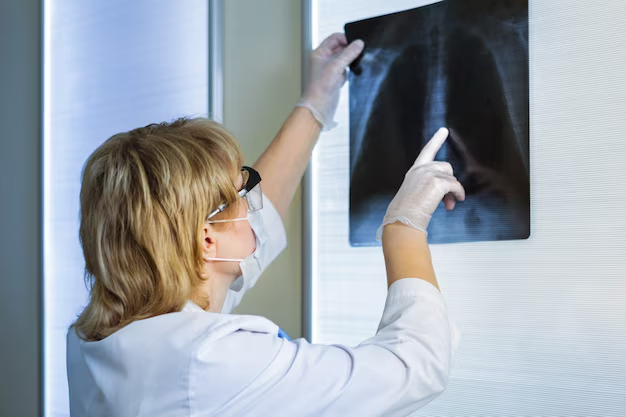
Uncovering the Diagnosis: The DEXA Scan
The primary tool for diagnosing osteoporosis is the Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) scan. This non-invasive procedure measures your bone mineral density (BMD), typically focusing on the hip, spine, and sometimes the forearm. A DEXA scan is quick, painless, and uses low-level X-rays to determine bone strength.
Once your BMD is evaluated, it is compared to the bone density of a healthy young adult of the same sex. This comparison results in what’s known as a T-score.
- T-score of -1.0 or above indicates normal bone density.
- T-score between -1.0 and -2.5 suggests low bone mass, or osteopenia, which is not yet osteoporosis but could progress.
- T-score of -2.5 or below confirms osteoporosis.
Understanding Risk Factors
Several risk factors could prompt a healthcare provider to recommend a DEXA scan:
- Women over 65 and men over 70
- Postmenopausal women under 65 with risk factors
- Adults who have suffered fragility fractures
- Those who have undergone long-term steroid therapy
Consulting a healthcare provider for a complete evaluation of risk factors can offer a more personalized recommendation.
What to Do After Diagnosis
A diagnosis of osteoporosis isn't the end of the road; it’s a new beginning for managing your health. Lifestyle changes are often the first recommendations, including:
- Increased calcium and vitamin D intake: Vital for bone health.
- Regular weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercises: Examples include walking, jogging, and weight lifting.
- Medication: Drugs that help prevent fractures might be prescribed, such as bisphosphonates or hormone-related therapy.
Exploring Financial and Educational Resources
Beyond health implications, pursuing the right financial support and educational resources is crucial for managing osteoporosis effectively. Various programs are available that can ease the financial burden:
Medicare and Medicaid: These government programs often cover the cost of DEXA scans if you qualify based on age and risk factors.
Patient Assistance Programs: Offered by pharmaceutical companies, these can help cover medication costs if you're financially eligible.
Supplemental Security Income (SSI): This provides financial assistance to those over 65, blind, or disabled under certain conditions.
Educational Grants and Scholarships: Numerous organizations offer grants and scholarships for individuals seeking to further educated on osteoporosis, providing both knowledge and skills to manage and live with the condition.
Helpful Resources to Explore 📚💸
- 🏥 Medicare & Medicaid Services: Check eligibility for free or reduced-cost DEXA scans.
- 🏛️ State Health Departments: Many states provide local aid programs to assist with healthcare expenses.
- 💊 Pharmaceutical Assistance Programs: Contact specific drug manufacturers to access discount or free medications.
- 📚 National Osteoporosis Foundation: Offers educational workshops and resources for those newly diagnosed.
- 🎓 Education Scholarships: Look into programs designed for furthering education about osteoporosis management and care.
Taking control of your bone health could lead to a stronger, more resilient future. With the right diagnosis and a strategic approach to managing both health and finances, living well with osteoporosis is truly within reach.
What You Get:
Free Osteoporosis FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about How Is Osteoporosis Diagnosed and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about How Is Osteoporosis Diagnosed topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Osteoporosis FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Nurse Is Caring For a Client Who Has Osteoporosis.
- a Percutaneous Is Performed To Treat Osteoporosis Related Compression Fractures
- Can Alcohol Cause Osteoporosis
- Can I Do Pilates If I Have Osteoporosis
- Can I Reverse Osteoporosis
- Can Men Get Osteoporosis
- Can Osteoporosis Affect Teeth
- Can Osteoporosis Be Cured
- Can Osteoporosis Be Painful
- Can Osteoporosis Be Reversed
