Your Guide to Does Medicare Cover Cochlear Implants
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Medicare FAQ and related Does Medicare Cover Cochlear Implants topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about Does Medicare Cover Cochlear Implants topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Medicare FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
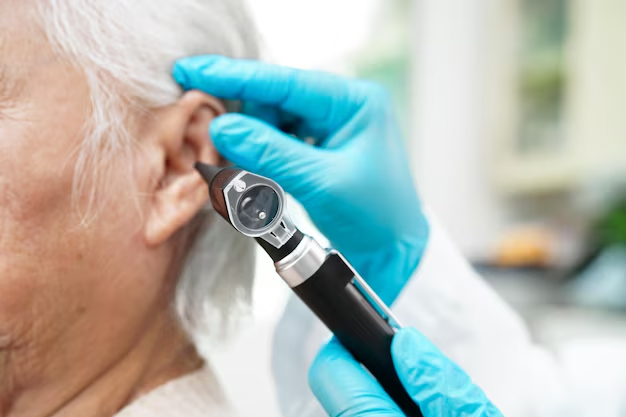
Can Medicare Help with Cochlear Implants? Here's What You Need to Know
For many individuals facing the challenge of significant hearing loss, cochlear implants offer a promising avenue for regaining a sense of sound. Yet, as hopeful as this medical advancement is, it often brings along the practical hurdle of cost. The critical question then becomes: Can Medicare cover cochlear implants? This question is particularly pertinent for older adults or those with significant health conditions that qualify for Medicare benefits. Let’s delve into the specifics and explore available financial support options for reducing the burdensome cost.
Understanding Medicare Coverage for Cochlear Implants
Medicare is a federal health insurance program primarily for people aged 65 and older, but also available for certain younger people with disabilities. When it comes to cochlear implants, the good news is that Medicare does provide some coverage. Generally speaking, if deemed medically necessary by a healthcare provider, cochlear implants are covered under Medicare Part B as they fall under durable medical equipment and prosthetic devices.
However, there are important caveats and considerations:
- Coverage Extent: Part B will generally cover 80% of the approved amount for doctor services, outpatient therapy, and some hospital outpatient services related to the implant procedure.
- Eligibility: The implant must be deemed necessary due to severe to profound hearing loss, usually backed by audiological and medical evaluations that Medicare might require.
- Out-of-Pocket Costs: Beneficiaries are responsible for the 20% coinsurance of the Medicare-approved amount, any remaining deductible, and possibly additional hospital costs depending on specifics of the procedure.
Navigating Financial Assistance Beyond Medicare
Given Medicare may not cover 100% of the costs, understanding additional financial assistance options is crucial:
Federal and State Aid Programs
For those who find themselves ineligible for full Medicare coverage or need additional financing, several governmental aids and state-specific programs can provide support. Programs like Medicaid, for those with low income, can often fill in the gaps where Medicare doesn't fully cover. Important to note, each state has its specific eligibility requirements and coverage details.
Considering Financial Aid and Debt Solutions
- Financial Aid: Look into non-profit organizations dedicated to supporting hearing-impaired individuals. They sometimes offer grants or scholarships for necessary procedures.
- Low-Interest Loans: Medical-specific low-interest loans might be a feasible route for covering upfront costs not managed by insurance.
Exploring Credit Options
- Credit Card Solutions: Contrary to conventional input, credit cards can be a strategic tool when managed wisely. Promotional 0% APR periods may offer breathing room to pay for healthcare costs without accruing additional interest.
Educational Grants and Supportive Community Resources
Educational programs can elevate awareness and resource accessibility, providing additional support for hearing-impaired individuals. Local resources and support groups often have invaluable insights and connections for creative financial solutions.
Ultimately, while the process of securing a cochlear implant—including all associated evaluations and surgery—can be overwhelming in complexity and cost, understanding the breadth of available resources is empowering.
💡 Financial Assistance Resources
- Medicaid: State-based aid for low-income individuals.
- Non-Profit Grants: Support from agencies like the Hearing Loss Association of America.
- State Disability Programs: Check eligibility for state-specific assistance.
- Specialized Loans: Medical financing companies offer tailored loans.
- 0% APR Credit Cards: Potential for interest-free payment plans.
- Community Support Groups: Networking can unveil additional resources.
Empowering yourself with knowledge about available Medicare coverage and other financial resources can help you take a confident step toward a future with improved hearing and a richer quality of life.
What You Get:
Free Medicare FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about Does Medicare Cover Cochlear Implants and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about Does Medicare Cover Cochlear Implants topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Medicare FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Medical Provider That Accepts Medicare Assignment Must
- a Medical Provider That Accepts Medicare Assignment Must Quizlet
- a Medicare Patient Received Treatment That Isn't Covered By Medicare
- a Medicare Patient Receives Treatment That Isn't Covered By Medicare
- a Medicare Supplement Basic Benefit Is Quizlet
- a Medicare Supplement Companies
- a Medicare Supplement Policy Is Quizlet
- a Medicare Supplement Policy Must Not Contain Benefits Which
- a Patient Received Treatment In August Medicare
- Am I Eligible For Medicare
