Your Guide to Where Can I Get a Hearing Test Near Me
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Hearing Aid FAQ and related Where Can I Get a Hearing Test Near Me topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about Where Can I Get a Hearing Test Near Me topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Hearing Aid FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Navigating Your Path to a Hearing Test: Where and How to Get Evaluated Locally
Are you starting to notice that you’re saying “What?” more than usual? Or are conversations in noisy environments becoming more challenging? It might be time to consider a hearing test. This comprehensive guide will help you understand where to get a hearing test near you and what to expect, providing valuable insights into this crucial aspect of maintaining your health and well-being.
📘 Understanding the Importance of Hearing Tests
Before diving into the "where," it's essential to grasp the “why.” Hearing tests are not just for those who suspect hearing loss; they're a critical component of routine healthcare. Regular examinations can catch potential issues early, allowing for timely intervention.
❓ Why Are Regular Hearing Tests Necessary?
- Early Detection of Hearing Loss: Identifying hearing decline early can prevent further loss and improve quality of life.
- Monitoring Existing Conditions: If you already have diagnosed hearing issues, regular tests help track your condition.
- Overall Health Indicator: Sometimes, hearing loss can be an early sign of other health issues, such as cardiovascular problems or diabetes.
🕒 How Often Should You Get a Hearing Test?
While specifics can vary depending on personal health factors and age, adults should generally aim for:
- Baseline Test: By age 21 if no symptoms exist earlier.
- Routine Checks: Every 3-5 years until age 50.
- Annual Tests: After age 50, or sooner if symptoms emerge.
Now that you understand the importance, let's explore how to access these vital services.
🏥 Finding a Hearing Test Provider Near You
When you're ready to take the step towards a hearing assessment, knowing where to go can ease the process. Various options exist, and choosing the right one depends on factors like convenience, insurance, and personal preference.
📍 Primary Care or Audiology Clinics
One of the most straightforward avenues for a hearing test is your primary care provider or specialized audiology clinics. Many primary healthcare centers have audiologists on staff, or they can refer you to one.
👉 Benefits of Audiology Clinics:
- Expertise: Audiologists specialize in hearing and balance disorders, ensuring expert care.
- Comprehensive Testing: Clinics offer detailed evaluations tailored to your needs.
- Access to Technology: They often have the latest equipment for accurate assessments.
🎯 Retail Hearing Centers and Pharmacies
Retail locations, including pharmacies and big-box stores, increasingly offer hearing tests. These setups often provide free or low-cost screening services.
👉 Pros:
- Accessibility: Quick and easy access without the need for appointments.
- Affordability: Lower costs, particularly useful for initial screenings.
- Convenience: Locations in community hubs mean minimal travel and waiting.
🏠 Mobile and Home-Based Services
For those unable to visit a location, mobile testing centers or home services could be a lifesaver. Certain services offer professional audiology care right at your doorstep.
👉 Advantages:
- Comfort: Familiar environment can ease anxiety associated with testing.
- Flexibility: Schedule according to your convenience without travel concerns.
- Comprehensive Care: Many services mirror those available in clinic settings.
🔍 Comparative Overview
Here’s a quick glance at the options to help you decide:
| Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Audiology Clinics | Expert care, comprehensive tests | Possible higher costs, need for appointments |
| Retail Hearing Centers | Accessible, affordable, no appointment needed | Limited to basic screenings |
| Mobile/Home Services | Comfort, flexibility, personalized care | Varied availability, possibly higher costs |
👂 What to Expect During a Hearing Test
Understanding what a hearing test involves can demystify the process. It can also help you prepare physically and mentally, making the experience smoother.
📋 Types of Hearing Tests
- Pure-Tone Testing: Measures your ability to hear sounds at different pitches and volumes.
- Speech Testing: Assesses how well you understand conversation at various volumes.
- Tympanometry: Evaluates the condition of the middle ear and mobility of the eardrum.
🕵️ Steps in a Hearing Assessment
- Pre-Test Consultation: Discuss your hearing history and any symptoms with the audiologist.
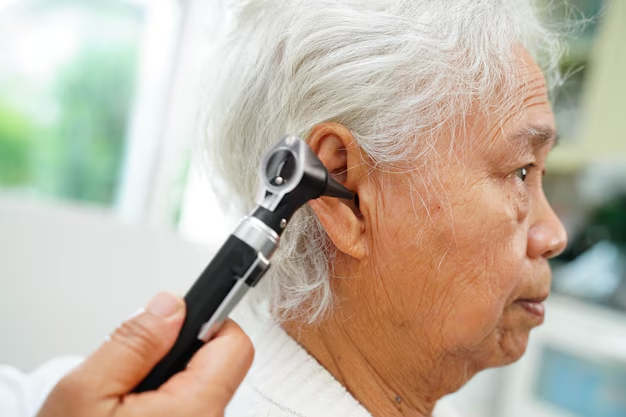
- Examination: Visual inspection of the ear for any physical conditions affecting hearing.
- Audiometric Test: Wearing headphones, different sounds are played to determine the quietest tones you can hear.
- Post-Test Discussion: Review results with your audiologist, who will offer insights into your hearing health.
🤔 After the Test: Understanding Results
Results from your hearing test will typically be available immediately. An audiologist will explain them comprehensively, identifying if there's any hearing loss and what steps, if any, should be taken next. Remember, following up as advised is critical to maintaining hearing health.
🤝 Connecting the Dots: What Steps to Take Post-Test
Once you have your results, strategize your next steps. Whether you require hearing aids, further medical evaluation, or simply peace of mind, knowing how to proceed ensures better outcomes.
🎯 Key Considerations
- Need for Hearing Aids: If recommended, consider consulting further with professionals regarding the best type for your needs.
- Insurance and Costs: Verify what tests and potential treatments are covered by your insurance plan.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regular follow-ups as advised to keep a pulse on any changes in your hearing.
💡 Practical Tips for Better Hearing Health
- Protect Your Ears: Use ear protection in loud environments.
- Stay Informed: Subscribe to reminders for routine hearing evaluations.
- Lifestyle Choices: Healthy diet and exercise contribute to better hearing.
📋 Quick Reference: Hearing Test Checklist ✅
To help streamline your journey towards better hearing, here’s a quick list of things to remember:
- ✨ Schedule Regular Tests: Routine checks catch potential issues early.
- 🏠 Explore Options: Choose a testing location that best fits your needs and comfort level.
- 🎧 Understand Test Processes: Familiarity with testing procedures helps ease the experience.
- 📞 Plan Post-Assessment Steps: Follow through with any recommended treatments or lifestyle adjustments.
✨ Wrapping Up: Navigating Your Hearing Health Journey
Ensuring your hearing stays at its best is a journey worth investing in. With a multitude of accessible resources available, taking the first step toward a hearing test is more convenient than ever. By actively engaging in regular hearing check-ups and considering proactive measures, you're paving the way for a future filled with sound awareness and enriched communication.
Use this guide as your blueprint for approaching hearing health with confidence, understanding, and preparedness. By making informed decisions today, you set the stage for maintaining your hearing health tomorrow and beyond.
What You Get:
Free Hearing Aid FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about Where Can I Get a Hearing Test Near Me and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about Where Can I Get a Hearing Test Near Me topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Hearing Aid FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Plus Hearing Aid Centers
- a Real Pain Showtimes Near Centerville
- Are Airpods Bad For Your Ears
- Are Apple Second Generation Airpods Hearing Aids
- Are Audien Hearing Aids Just Amplifiers
- Are Costco Hearing Aids As Good As Others
- Are Costco Hearing Aids Good
- Are Hearing Aid Domes Interchangeable
- Are Hearing Aid Subscriptions Worth It
- Are Hearing Aid Tax Deductible
