Your Guide to What Is a Hearing Aid
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Hearing Aid FAQ and related What Is a Hearing Aid topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about What Is a Hearing Aid topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Hearing Aid FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Discovering Hearing Aids: What You Need to Know
The world is full of sounds — the chime of a doorbell, the laughter of a child, or the melody of a favorite song. But for those with hearing loss, these sounds can become muted or altogether absent. Hearing aids offer a practical solution, providing the gift of sound to improve quality of life. If you're wondering what a hearing aid is and how it can help, you're in the right place. Let's explore this vital piece of technology, which is a lifeline for many.
🔍 Understanding Hearing Aids
What Exactly Is a Hearing Aid?
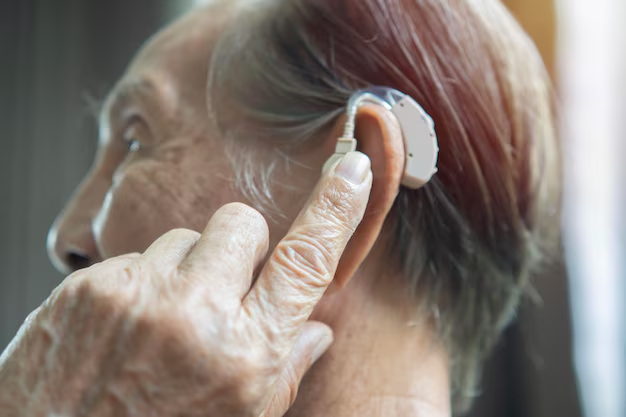
A hearing aid is a small electronic device designed to amplify sound and make it more accessible to individuals with hearing impairments. Positioned in or around the ear, these devices amplify sounds, making them easier to hear and understand.
Key Components of a Hearing Aid:
- Microphone: Captures sound from the environment.
- Amplifier: Increases the volume of the captured sound.
- Speaker: Delivers the amplified sound to the ear.
- Battery: Powers the device, usually replaceable or rechargeable.
How Do Hearing Aids Work?
The mechanics of a hearing aid are simple yet effective:
- Capture: The microphone picks up sounds around the wearer.
- Processing: The sounds are processed and converted into digital signals.
- Amplification: The signals are amplified based on the wearer’s specific hearing needs.
- Output: The amplified signals are sent to the ear through the speaker.
By enhancing sounds, hearing aids bridge the gap for those experiencing hearing loss, often due to age or other medical conditions.
🎯 Types of Hearing Aids
Hearing aids come in several styles and forms, each suited to different preferences and levels of hearing loss.
Behind-the-Ear (BTE) Hearing Aids
BTE devices rest behind the ear, with a tube directing sound into the ear canal. They are versatile and powerful, accommodating a wide range of hearing losses.
In-the-Ear (ITE) Hearing Aids
Fitting entirely inside the outer ear, ITE hearing aids offer a more discreet design. They are suitable for mild to severe hearing loss but must be custom-fitted to the wearer’s ear.
In-the-Canal (ITC) and Completely-in-Canal (CIC) Hearing Aids
These are the smallest and most inconspicuous hearing aids available. ITC and CIC devices fit partly or completely inside the ear canal, making them less visible but also more susceptible to earwax and moisture.
Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) Hearing Aids
Similar to BTE devices, RIC hearing aids place the receiver (speaker) inside the ear canal, connected by a thin wire. They provide comfortable and open-fit designs for a natural sound experience.
🧐 Deciding If You Need a Hearing Aid
Recognizing Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can be gradual, making it difficult to recognize at first. Here are some common indicators:
- Difficulty following conversations, especially in noisy environments.
- Frequently asking others to repeat themselves.
- Increased volume on TVs or phones.
- Avoidance of social situations due to difficulty in hearing.
Consider a Hearing Test
If you notice these signs, a hearing test conducted by a professional can confirm the extent of hearing loss and the potential benefit of using a hearing aid.
Benefits of Using Hearing Aids
- Improved Communication: Enhances ability to follow conversations and engage with others.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Reduces feelings of isolation and improves overall mental health.
- Increased Safety: Awareness of sounds like alarms and alerts can prevent accidents.
👂 Features and Advancements in Hearing Aids
Modern hearing aids are packed with advanced features that were unimaginable a decade ago.
Noise Reduction
Many hearing aids now include technology that filters background noise, making speech clearer and reducing strain during conversations.
Connectivity
With Bluetooth capabilities, hearing aids can connect directly to smartphones, laptops, and TVs, providing a seamless audio experience.
Rechargeable Batteries
These save the hassle and cost of constantly replacing batteries, offering eco-friendly solutions without compromising on power.
Personalized Settings
Advanced hearing aids can be configured to adapt to different environments, automatically adjusting the amplification based on presets.
💡 Choosing the Right Hearing Aid
Consult a Hearing Specialist
Before purchasing a hearing aid, consult with a certified audiologist or hearing specialist. They will assess your hearing needs and recommend the best device for you.
Key Considerations
- Lifestyle Needs: Consider how active you are and the environments you frequent.
- Budget: Hearing aids range widely in price, so determine what fits within your financial plan.
- Comfort and Fit: Comfort is crucial as you'll be wearing the device for extended periods.
📝 Summary: Key Takeaways for Hearing Aid Users
Here’s a concise list of important points to consider when thinking about hearing aids:
- 🔊 Versatile Options: From BTE to CIC, the type of hearing aid can impact comfort and performance.
- 🦻 Regular Maintenance: Keep your hearing aids clean and dry to ensure longevity.
- 🔋 Choose Wisely: Depending on personal preferences, opt for either disposable or rechargeable batteries.
- 📱 Tech Savvy: Leverage features like Bluetooth connectivity for an enriched audio experience.
- 👨⚕️ Professional Guidance: Work closely with hearing healthcare providers to tailor the device to your needs.
Looking Forward with Hearing Aids
Choosing a hearing aid can be a life-changing decision, offering significant improvements in personal and social well-being. With technology constantly evolving, today’s hearing aids not only enhance hearing but also integrate effortlessly with our digital lives. If hearing loss is affecting you or someone you love, delving into the world of hearing aids might be the next step towards a richer, more connected experience. Discover how sound can open doors to a more vibrant life—one conversation, one song, and one moment at a time.
What You Get:
Free Hearing Aid FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about What Is a Hearing Aid and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about What Is a Hearing Aid topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Hearing Aid FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Plus Hearing Aid Centers
- a Real Pain Showtimes Near Centerville
- Are Airpods Bad For Your Ears
- Are Apple Second Generation Airpods Hearing Aids
- Are Audien Hearing Aids Just Amplifiers
- Are Costco Hearing Aids As Good As Others
- Are Costco Hearing Aids Good
- Are Hearing Aid Domes Interchangeable
- Are Hearing Aid Subscriptions Worth It
- Are Hearing Aid Tax Deductible
