Your Guide to How To Get Hearing Aids
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Hearing Aid FAQ and related How To Get Hearing Aids topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about How To Get Hearing Aids topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Hearing Aid FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Navigating the Path to Hearing Aids: Your Comprehensive Guide
Hearing loss can sneak up on anyone, gradually making its presence felt by turning the volume of life down just a notch. Suddenly, conversations become mumbles, music seems muted, and everyday sounds fade into whispers. Fortunately, hearing aids can make a world of difference, transforming these silent struggles back into vibrant auditory experiences. But how do you actually go about obtaining hearing aids? This guide will illuminate the steps to acquiring these crucial devices, opening up a world of sound once more.
Understanding Hearing Loss
Identifying Symptoms of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss often progresses slowly, and recognizing early signs can be challenging. Common indicators include frequently asking others to repeat themselves, having difficulty hearing in noisy environments, or needing to raise the volume on electronic devices unusually high. Recognizing these symptoms early can significantly affect treatment outcomes.
Differentiating Types of Hearing Loss
Understanding the type of hearing loss you're experiencing is vital for treatment. There are generally three types:
- Conductive Hearing Loss: Issues in the outer or middle ear, often treatable medically or surgically.
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Damage to the inner ear or nerve pathways, usually requiring hearing aids.
- Mixed Hearing Loss: A combination of both, necessitating a more comprehensive approach.
Exploring Your Hearing Aid Options
Types of Hearing Aids
Hearing aids come in various styles, each offering unique benefits:
- Behind-The-Ear (BTE): Suitable for most types of hearing loss and easy to handle.
- In-The-Ear (ITE): Custom-fit and offer features like volume control.
- In-The-Canal (ITC) & Completely-In-The-Canal (CIC): Less visible and often preferred for mild to moderate hearing loss.
Understanding the pros and cons of each type can empower you to make an informed choice.
Factors to Consider
When exploring hearing aid options, consider:
- Lifestyle Needs: Consider how your daily activities might impact your choice. Are you frequently in noisy environments?
- Technological Features: Today's hearing aids offer Bluetooth connectivity and rechargeable batteries, enhancing user experience.
- Budget Constraints: Hearing aids can be a significant investment. Exploring different models and their features will help balance cost and functionality.
The Process of Getting Hearing Aids
Step 1: Scheduling a Hearing Test
The first step in acquiring hearing aids is a comprehensive hearing evaluation by an audiologist. This test will determine the degree and type of your hearing loss, guiding your options moving forward.
Preparing for Your Test
Before the test, think about your hearing experiences in different situations. This preparation allows the audiologist to tailor recommendations to your specific needs.
Step 2: Consultation with an Audiologist
Post-evaluation, a detailed consultation with your audiologist will cover potential solutions, types of hearing aids suited to your loss, and a discussion about realistic expectations.
Step 3: Selecting Your Hearing Aids
Based on the consultation, you can choose the hearing aids that best fit your needs and budget. You may have the opportunity to try different models to see which feels most comfortable.
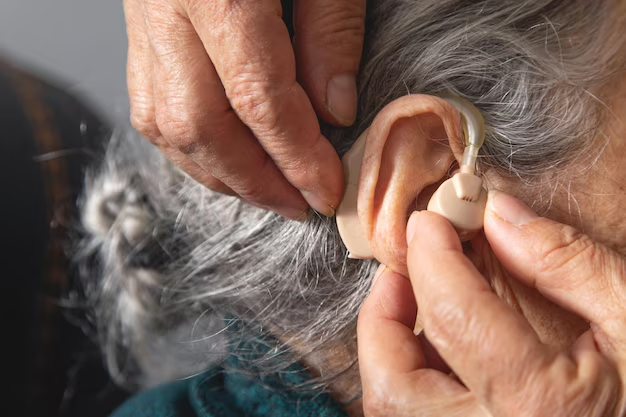
Step 4: Fitting and Adjustment
Once selected, hearing aids will be custom-fitted and adjusted. This process might involve multiple visits to ensure optimal comfort and performance.
Step 5: Adapting to Hearing Aids
Adjustment periods are normal. You may experience a learning curve as your brain acclimates to hearing through the aids. Patience and persistence are key during this period.
🏷️ Quick Tips for First-Time Hearing Aid Users:
- Be Patient: Initial discomfort or unfamiliarity is normal; give yourself time to adjust.
- Practice Hearing in Various Settings: Gradually introduce yourself to different listening environments.
- Follow-up Appointments: Regular visits to your audiologist ensure your hearing aids are fine-tuned for peak performance.
Cost and Insurance Considerations
Understanding Pricing
Hearing aids can range significantly in price, often reflecting the technology and features offered. While investing in higher-end models may seem daunting, the enhanced quality of life they provide can be invaluable.
Insurance and Financial Assistance
Coverage for hearing aids varies. Some insurance plans or government programs may offer support, but it's essential to research what's available in your area. Often, payment plans or financial assistance can help ease the financial burden.
Comparison Shop
Consider visiting multiple hearing aid providers or retailers. Comparing features, warranties, and costs can ensure you get the best deal possible.
Maintaining Your Hearing Aids
Daily Care and Maintenance
Proper care of hearing aids prolongs their life and ensures they function correctly. Basic maintenance includes regular cleaning and checking for moisture build-up.
Regular Check-ups
Routine check-ups with your audiologist can catch any performance issues early and make necessary adjustments to improve the performance of your hearing aids.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Understanding common issues, like feedback or reduced sound quality, can prevent minor problems from becoming significant concerns. Learning some basic troubleshooting steps can save time and frustration.
Embracing Life with Hearing Aids
Enhancing Communication
Hearing aids reopen lines of communication, allowing for effortless interactions in personal and professional settings. Tips for communicating effectively include speaking clearly, ensuring good lighting, and minimizing background noise.
Participating in Social Activities
With improved hearing, social activities become more enjoyable. Whether it's going to the theater, dining out, or enjoying music, hearing aids enhance the richness and enjoyment of these experiences.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Hearing aids often result in improved mood and social interactions, reducing the feelings of isolation associated with hearing loss. Embracing these changes can positively impact mental health and overall quality of life.
Summary of Steps to Get Hearing Aids 🎯
- Identify Symptoms: Noticeable changes in hearing should prompt a hearing evaluation.
- Understand Your Hearing Loss: Different types of hearing loss require different solutions.
- Schedule a Hearing Test: Consult with an audiologist for a comprehensive evaluation.
- Consultation and Selection: Choose hearing aids that fit your lifestyle and budget.
- Fitting and Adjustment: Ensure your hearing aids are custom-fitted for optimal performance.
- Adaptation Period: Allow time to get used to your new hearing aids.
By following these steps, you can effectively navigate the process of acquiring hearing aids, reclaiming the full spectrum of sounds life has to offer. Whether you're a first-time user or looking to upgrade, this guide aims to help you make informed decisions with confidence and clarity.
What You Get:
Free Hearing Aid FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about How To Get Hearing Aids and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about How To Get Hearing Aids topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Hearing Aid FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Plus Hearing Aid Centers
- a Real Pain Showtimes Near Centerville
- Are Airpods Bad For Your Ears
- Are Apple Second Generation Airpods Hearing Aids
- Are Audien Hearing Aids Just Amplifiers
- Are Costco Hearing Aids As Good As Others
- Are Costco Hearing Aids Good
- Are Hearing Aid Domes Interchangeable
- Are Hearing Aid Subscriptions Worth It
- Are Hearing Aid Tax Deductible
