Your Guide to How Does Hearing Aid Work
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Hearing Aid FAQ and related How Does Hearing Aid Work topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about How Does Hearing Aid Work topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Hearing Aid FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Understanding How Hearing Aids Work: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever marveled at how hearing aids can transform whispered sounds into clear conversations? For those experiencing hearing challenges, hearing aids offer a lifeline to better communication and an improved quality of life. This article delves into the intricate workings of hearing aids, offering insight into how these tiny devices can make such a significant impact.
The Basics of Hearing Aids
Hearing aids are sophisticated devices designed to amplify sound for individuals with hearing impairment. At their core, hearing aids work by making sounds louder and clearer, allowing users to better engage with the world around them.
Key Components of Hearing Aids 🦻
Understanding how a hearing aid works involves familiarizing oneself with its essential components:
- Microphone: Captures sound from the environment.
- Amplifier: Increases the volume of sound.
- Speaker (Receiver): Delivers the amplified sound to the ear.
- Battery: Powers the device, enabling continuous operation.
- Control Chips: Processes sound signals for clarity and adjustment.
Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring that sound is transmitted effectively, allowing users to hear more acutely.
How Sound Travels Through a Hearing Aid
The process begins with the microphone picking up sounds, which are then converted into electrical signals. These signals are processed by the control chips, which adjust them for volume and clarity. The amplifier then boosts these signals before they are delivered by the speaker into the ear canal. This seamless transformation of sound ensures users receive both clarity and comfort.
Types of Hearing Aids
Hearing aids come in various styles, each tailored to different needs and preferences. Let’s explore the most common types:
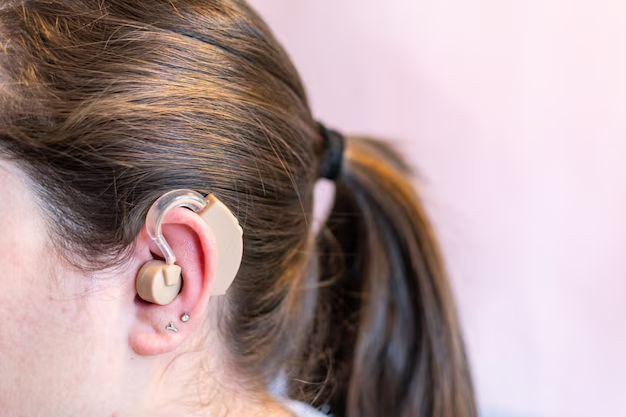
Behind-the-Ear (BTE)
BTE hearing aids are worn behind the ear and connected to a custom earpiece inside the ear canal. They’re suitable for people of all ages and cater to a range of hearing losses.
In-the-Ear (ITE)
ITE hearing aids fit entirely inside the outer ear and are suitable for mild to severe hearing loss. They are custom-made to fit the user’s ear, providing a more discrete solution.
In-the-Canal (ITC) and Completely-in-Canal (CIC)
These smaller hearing aids fit partly or completely within the ear canal, providing a very discrete option. ITC and CIC aids are typically for mild to moderate hearing loss.
Receiver-in-Canal (RIC)
RIC hearing aids have a receiver or speaker in the ear canal, connected to the device by a thin wire. They offer a natural sound quality due to their design, making them quite popular.
Advanced Features and Technologies
Hearing aids have evolved dramatically, embracing advanced technologies that enhance user experience:
Noise Reduction and Speech Enhancement
Modern hearing aids can differentiate between speech and noise, providing noise reduction capabilities. This ensures clearer conversations even in challenging listening environments.
Directional Microphones
Directional microphones focus on sounds coming from a specific direction, usually the front, which is useful in noisy settings, improving the ability to hear speech in crowded places.
Connectivity Features
Bluetooth-enabled hearing aids allow users to connect directly with smartphones and other devices. This feature supports music streaming and phone calls directly through the hearing aid.
Smartphone Apps and Remote Controls
Many hearing aids are equipped with smartphone apps or remote controls for easy adjustment of settings. This feature adds convenience, letting users personalize their listening experience on-the-go.
Selecting the Right Hearing Aid
Choosing the right hearing aid can significantly impact the user’s experience. Here are a few considerations:
Level of Hearing Loss
The degree and type of hearing loss will guide which hearing aid style is most suitable. Hearing professionals can conduct assessments to recommend the best options.
Lifestyle Needs
Consider the environments where the hearing aid will be used. For active lifestyles or those frequently in noisy environments, options with advanced noise reduction and automatic sound adjustment might be beneficial.
Comfort and Discretion
Comfort is key for something worn daily. Some users prioritize smaller, less visible options, while others may focus on enhanced sound features.
Budget and Insurance
Hearing aids can vary widely in cost. It's important to consider budget constraints and explore insurance options that may cover some of the costs.
Common Myths About Hearing Aids
There are several misconceptions about hearing aids that can lead to misinformation:
- Hearing aids restore normal hearing: While they significantly enhance hearing abilities, they do not restore hearing to normal levels.
- One hearing aid is sufficient: For individuals with hearing loss in both ears, wearing two aids provides a balanced and natural hearing experience.
- They’re only for older adults: Hearing aids benefit people of all ages with hearing loss, including children and younger adults.
Practical Tips for Hearing Aid Users
Using hearing aids effectively requires some adaptation. Here are practical tips for maximizing their benefits:
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular cleaning prevents buildup that can obstruct sound. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for best practices.
Battery Management
Hearing aids require regular battery changes. Built-in indicators will alert users when battery levels are low, ensuring continuous function.
Follow-Up Appointments
Scheduling regular follow-up appointments with audiologists helps maintain optimal performance. These visits can include adjustments based on changing hearing needs.
Practice Patience
Adapting to hearing aids can take time. Consistently wearing them throughout the day helps the brain adjust to the new sound quality.
A Quick Summary of Key Points 📝
Here’s a quick glance at the essential aspects of hearing aids:
- Key Components: Microphones, amplifiers, receivers — all work together to enhance sound.
- Types and Styles: BTE, ITE, ITC, CIC, and RIC cater to diverse needs.
- Advanced Technologies: Noise reduction, directional microphones, Bluetooth connectivity for personalized listening.
- Choosing Wisely: Factor in hearing loss level, lifestyle, comfort, and budget.
- Addressing Myths: Understand their limitations and potential for improved quality of life.
- Usage Tips: Regular maintenance, follow-up care, and patience are key for successful adaptation.
The Future of Hearing Aids
As technology continues to advance, hearing aids are expected to become even more sophisticated, offering users enhanced sound quality, greater comfort, and increased integration with other technologies. The future of hearing aids not only lies in better hearing but elevating overall user experience and satisfaction.
In conclusion, understanding how hearing aids work provides a framework for appreciating the profound benefits they offer. For those experiencing hearing loss, these devices are not merely tools but companions on the journey to improved communication and enriched daily experiences.
What You Get:
Free Hearing Aid FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about How Does Hearing Aid Work and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about How Does Hearing Aid Work topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Hearing Aid FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Plus Hearing Aid Centers
- a Real Pain Showtimes Near Centerville
- Are Airpods Bad For Your Ears
- Are Apple Second Generation Airpods Hearing Aids
- Are Audien Hearing Aids Just Amplifiers
- Are Costco Hearing Aids As Good As Others
- Are Costco Hearing Aids Good
- Are Hearing Aid Domes Interchangeable
- Are Hearing Aid Subscriptions Worth It
- Are Hearing Aid Tax Deductible
