Your Guide to How To Care For a Diabetic Senior Cat At Home
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about For Seniors FAQ and related How To Care For a Diabetic Senior Cat At Home topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about How To Care For a Diabetic Senior Cat At Home topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to For Seniors FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
How to Best Care for Your Senior Cat with Diabetes at Home
Caring for a senior cat brings unique joys and challenges. When you add diabetes into the mix, you might feel a bit overwhelmed. However, with the right approach, you'll discover that managing your cat's health can become a rewarding part of your daily routine. Whether you’re new to caring for a diabetic cat or looking to improve your existing care practices, this guide is packed with insights to make your journey smoother.
Understanding Feline Diabetes
What is Feline Diabetes?
At its core, feline diabetes is similar to human diabetes. It's a condition in which a cat's pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin or their bodies don’t respond properly to insulin. Insulin is crucial as it helps regulate the amount of glucose (sugar) in the bloodstream. Without effective insulin production or response, cats can experience elevated blood sugar levels, leading to various health complications.
Symptoms to Watch For
Awareness is your first step. Early recognition can make a significant difference:
- Increased Thirst and Urination: You'll notice your cat drinking and urinating more frequently.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite a voracious appetite, your cat may start losing weight.
- Lethargy and Weakness: Cats may become less active or act lethargic.
- Poor Coat Condition: Your cat's fur could become dry or look unkempt.
If you notice these signs, consult a veterinarian to confirm any suspicions and discuss appropriate next steps.
Creating a Diabetes-Friendly Environment at Home
Dietary Adjustments
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing diabetes. Most experts suggest a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet. Here’s why:
- High-Protein Foods: They support muscle mass and aid in satiety, reducing excessive food intake.
- Low-Carb Options: Help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Tip: Avoid free-feeding. Instead, establish a regular feeding schedule to keep your cat’s blood sugar stable.
Essential Home Adjustments
Make your home a sanctuary for your diabetic cat:
- Accessible Litter Boxes: As they may urinate more, multiple litter boxes around the home can be helpful.
- Comfortable Sleeping Areas: Ensure they have warm, comfortable spots to rest.
- Easy-to-Reach Food and Water: Consider elevated dishes to reduce strain on their necks.
Monitoring and Routine Care
Regular Testing
Maintaining your cat’s health requires regular monitoring:
- Blood Glucose Testing: You can perform these at home using a glucometer designed for pets. It helps track your cat’s glucose levels, guiding dietary and medical decisions.
- Routine Vet Visits: Regular check-ups are crucial for tracking progress and making necessary adjustments.
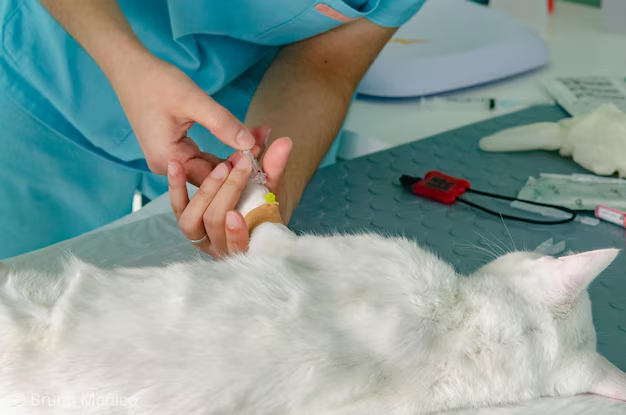
Administering Insulin
For many diabetic cats, insulin injections become part of daily life. Here are some simple tips for administering:
- Stay Calm: Your cat senses your energy. A calm demeanor means a smoother experience for you both.
- Routine Timing: Administer insulin at the same times each day to maintain blood spikes and crashes.
- Positive Reinforcement: Offer a small treat post-injection to build positive associations.
Lifestyle and Engagement
Encouraging Physical Activity
Activity levels can affect weight and blood glucose levels:
- Interactive Toys: Engage with toys that stimulate hunting instincts.
- Short Play Sessions: Multiple, short sessions are better than long, tiring playtimes.
- Outdoor Exploration: If safe, supervised outdoor time can stimulate them mentally and physically.
Emotional Well-being
Don’t forget the emotional aspect:
- Routine and Stability: Cats thrive on routine. Consistent feeding and playtimes can reduce stress.
- Gentle Grooming: Regular brushing not only improves coat condition but strengthens your bond.
Creating Your Care Checklist
To keep everything on track, a checklist can be a fantastic tool. Here's a simple layout:
📋 Daily Care Checklist for Your Diabetic Cat
🕒 Feeding Schedule
- Morning:
- Offer a high-protein, low-carb breakfast.
- Check water levels.
- Evening:
- Dinner setup.
- Check water levels.
- Morning:
💉 Insulin Administration
- Morning Injection:
- Prepare insulin dose.
- Administer calmly and gently.
- Offer a small treat.
- Evening Injection:
- Prepare insulin dose.
- Administer the same as morning.
- Morning Injection:
📏 Health Monitoring
- Weekly:
- Weigh your cat.
- Conduct a blood glucose test.
- Monthly:
- Schedule a vet check-up.
- Weekly:
🎾 Activity & Engagement
- Daily:
- Engage in two short play sessions.
- Offer interactive toys.
- Weekly:
- Set up safe outdoor exploration for mental enrichment.
- Daily:
Final Considerations and Insights
Caring for a senior cat with diabetes involves patience and love. While it might seem daunting at first, once you establish a routine, it can become a meaningful experience that strengthens your bond. Remember, every cat is unique, and understanding your feline friend's specific needs will guide your journey.
Empathy, consistency, and constant observation are key. Your dedication to providing the best care ensures your senior cat can continue to enjoy their golden years comfortably and happily. In the process, you’ll find that you gain just as much from this journey as they do. 🌟
What You Get:
Free For Seniors FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about How To Care For a Diabetic Senior Cat At Home and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about How To Care For a Diabetic Senior Cat At Home topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to For Seniors FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Haiku For a Graduating Senior
- a Senior Citizen Id Card Is Valid For 10 Years.
- Are Edibles Safe For Seniors
- Are Keto Gummies Safe For Seniors
- Are Keto Pills Safe For Seniors
- Are There Any Federal Programs For Seniors To Get Internet
- Are There Really Special Officers For Senior Citizens On Cars
- Are There Really Zero Premium Drug Plans For Seniors
- Are Yak Chews God For Senior Dogs
- Can Opener For Seniors
