Your Guide to What Is The Ingredients Used To Make Dentures
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Dentures FAQ and related What Is The Ingredients Used To Make Dentures topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about What Is The Ingredients Used To Make Dentures topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Dentures FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Exploring the Ingredients Behind Dentures: What You Should Know
When it comes to oral health solutions, dentures have been a longstanding option for those who have lost their natural teeth. They offer not only aesthetic benefits but also functionality to help individuals maintain a normal lifestyle. But have you ever wondered what exactly goes into making these essential oral appliances? Understanding the ingredients used in dentures can help demystify the process and provide insight into why they work so well.
The Basics of Denture Composition
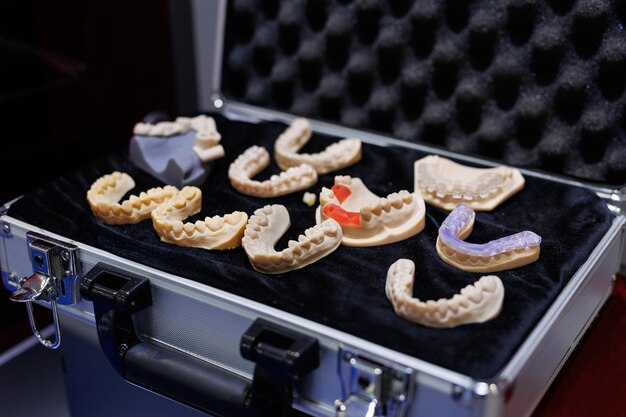
Dentures, also known as false teeth, are typically composed of two main parts: the denture base and the artificial teeth. The materials used must be both durable and comfortable, ensuring the dentures can withstand daily use while fitting comfortably within the mouth.
Materials for the Denture Base
The denture base acts as the foundation for the artificial teeth and is designed to sit on or against the gums comfortably. Here's a look at the primary materials used:
Acrylic Resin:
- Pros: Lightweight and can be colored to match the natural gum color, offering a more aesthetically pleasing appearance.
- Cons: While durable, they might not be as strong as other materials used in partial denture bases.
Metal: Often used in partial dentures, metals like cobalt-chromium or stainless steel offer greater strength.
- Pros: More durable and thinner, providing a less bulky feel.
- Cons: Not as aesthetically flexible as acrylic.
Flexible Polymers: These materials provide an alternative to traditional rigid bases.
- Pros: Offer a more comfortable fit and are less likely to break.
- Cons: Generally used for specific cases where flexibility is necessary.
Artificial Teeth Material
The teeth themselves must not only look natural but be able to endure the forces of chewing. Here's what is commonly used:
Acrylic Resin:
- Pros: Can be easily shaped and colored to look like natural teeth and provide a good level of wear resistance.
- Cons: Although strong, they may wear down faster than ceramic options.
Ceramic or Porcelain:
- Pros: Highly durable and stain-resistant, providing a natural-looking translucency similar to tooth enamel.
- Cons: Can be heavier than acrylic and generally more expensive.
The Process of Making Dentures
Understanding the ingredients leads naturally into the process of how dentures are made, providing insight into why certain materials are chosen.
Step-by-Step Denture Creation
Initial Consultation and Impressions:
- Objective: To understand the patient's needs and make initial impressions of the oral cavity.
- Materials: Impression trays and special dental putty.
Model Creation:
- Objective: Creating an accurate model of the mouth to plan the denture’s size and fit.
- Materials: Plaster or digital scanning for creating a cast.
Wax Model and Try-In:
- Objective: Create a wax model with temporary teeth for fitting and adjustment.
- Materials: Wax and acrylic teeth in a preliminary setup.
Final Denture Production:
- Objective: Fabrication using chosen materials to complete the dentures.
- Process: Includes curing acrylic resin or metal frameworks, attaching artificial teeth, and polishing.
Adjustment and Maintenance
Once the dentures are ready, they are fitted to the patient. Adjustments may be necessary to ensure comfort and proper function. Long-term maintenance includes regular cleaning and routine dental check-ups to ensure the denture's ongoing suitability.
Different Types of Dentures and Their Ingredients
Dentures can be tailored to specific needs, ranging from complete sets for full tooth loss to partials that fill in gaps.
Complete Dentures
- Purpose: Replace all teeth in the upper or lower jaw.
- Material Use: Predominantly acrylic for both base and teeth to provide an aesthetically pleasing and functional solution.
Partial Dentures
- Purpose: Fill in gaps of missing teeth, preserving the position of remaining natural teeth.
- Material Use: Often include metal frameworks for added strength and flexibility.
Implant-Supported Dentures
- Purpose: Combine dentures with dental implants for improved stability.
- Material Use: Typically involve titanium implants, with denture materials as discussed earlier.
Myths and Facts About Dentures
With a comprehensive understanding of their ingredients and processes, it's essential to debunk myths commonly associated with dentures:
*️⃣ Myth: Dentures are only for the elderly.
- Fact: Dentures are used by individuals of all ages who have lost teeth due to various reasons such as accidents or illness.
*️⃣ Myth: All dentures look fake.
- Fact: Modern dentures use advanced materials and techniques to offer highly realistic and aesthetically pleasing results.
Key Takeaways for Consumers
Understanding the composition and process of making dentures can empower consumers to make informed decisions. Here are some practical tips and considerations:
🔹 Material Matters: Consider the pros and cons of different materials based on your lifestyle and needs—whether you prioritize durability, aesthetics, or comfort.
🔹 Consultation is Key: Work with dental professionals to understand the best options for you. A good fit and choice of materials can make a significant difference.
🔹 Regular Maintenance: Like natural teeth, dentures require cleaning and maintenance to ensure longevity and hygiene.
🔹 Customization Options: Explore options for personalized fittings and aesthetic choices, such as choosing between different types of artificial teeth.
Visual Summary: Quick Tips for Denture Materials
Here’s a concise summary of important considerations for selecting denture materials:
| Material | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Acrylic Resin | Lightweight, color-matching, cost-effective | May wear down quicker than ceramic, less durable |
| Metal | Strong, less bulky | Less aesthetic flexibility, can be heavier |
| Ceramic/Porcelain | Durable, stain-resistant, natural appearance | Heavier, more expensive |
| Flexible Polymers | Comfortable fit, break-resistant | Limited use to specific denture types |
By arming yourself with the right knowledge and understanding the composition of dentures, you can approach the decision-making process with confidence. Whether it's selecting the right material or understanding the process involved, these insights can significantly enhance your experience with dentures and contribute to long-term oral health and satisfaction.
What You Get:
Free Dentures FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about What Is The Ingredients Used To Make Dentures and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about What Is The Ingredients Used To Make Dentures topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Dentures FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Bridge For Teeth
- a Denture Plan That You Can Pay Monthly Payments
- Are Dentures Covered By Insurance
- Are Dentures Covered By Medicare
- Are Dentures Uncomfortable
- Are Permanent Dentures Thinner Than Temporary Dentures
- Are Snap-in Dentures Covered By Insurance
- Are There Plastic Dental Partials With Metal
- Can a Tooth Be Added To a Valplast Denture
- Can Dogs Get Dentures
