Your Guide to What Is Vascular Dementia Disease
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Dementia FAQ and related What Is Vascular Dementia Disease topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about What Is Vascular Dementia Disease topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Dementia FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Understanding Vascular Dementia: What You Need to Know
Vascular dementia is a term you might have come across in discussions about cognitive health, especially if you or a loved one is experiencing memory issues or challenges with thinking skills. This guide is your go-to resource for understanding what vascular dementia is, what causes it, and what you can do to approach this condition with informed confidence.
What Is Vascular Dementia?
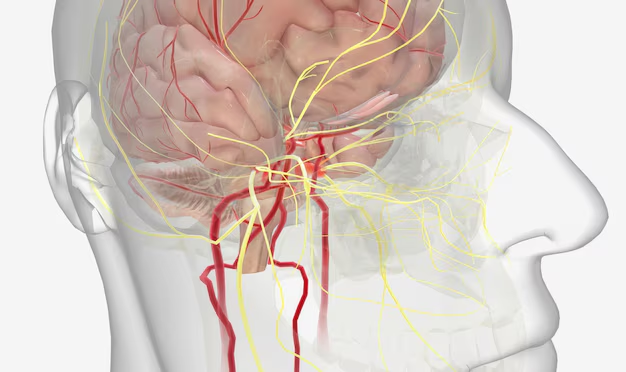
Vascular dementia is a form of dementia caused by reduced blood flow to the brain, affecting cognitive functions such as memory, reasoning, and problem-solving. The impact on cognitive abilities depends on the specific areas of the brain affected. Understanding this condition begins with knowing the basics of how it differs from other types of dementia.
Difference Between Vascular Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease
While both are types of dementia, vascular dementia and Alzheimer's disease have different underlying causes. Alzheimer's is mainly associated with the build-up of plaques and tangles in the brain, whereas vascular dementia results from problems in blood supply. Differentiating the two can help in targeting the right management strategies.
Causes and Risk Factors
Vascular dementia is primarily caused by conditions that block or reduce blood flow to brain regions, depriving them of oxygen and nutrients. Here's a closer look at the causes and risk factors:
- Stroke: A significant cause, strokes can block an artery in the brain.
- Narrowed or Chronically Damaged Blood Vessels: Conditions like atherosclerosis can lead to reduced blood flow.
- Heart Health Issues: Conditions like high blood pressure, heart attack, diabetes, and high cholesterol increase risk.
Key Risk Factors
- Age: Older age increases the risk.
- History of Heart Disease: Those with cardiovascular problems have a higher risk.
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, inactivity, and poor diet can elevate risk.
Recognizing Symptoms of Vascular Dementia
Awareness of symptoms is crucial for early recognition. While symptoms can vary, here are common indicators of vascular dementia:
- Confusion: Especially immediate or short-term confusion.
- Disinterest in Daily Activities: Reduced ability to organize thoughts or activities.
- Difficulty with Attention: Trouble focusing or concentrating.
- Memory Loss: More noticeable after a stroke.
- Difficulty with Visuospatial Skills: Problems judging distances or difficulties in motor coordination.
📝 Quick Symptom Checklist
- 📉 Loss of attention and concentration
- 🧠 Memory issues
- 🔄 Sudden personality changes
- 📅 Challenges in following simple directions
Diagnosis of Vascular Dementia
Diagnosing vascular dementia can be complex, involving several steps to differentiate it from other forms of dementia. Here's how the process usually unfolds:
- Medical History Review: Understanding symptoms and past medical events.
- Physical and Neurological Exam: Evaluating overall health and cognitive functions.
- Brain Imaging Scans: Techniques like MRI or CT scans to look for changes.
- Cognitive Tests: Assessments to gauge ability to think, reason, and remember.
Early diagnosis can be beneficial in managing symptoms and planning for a better quality of life.
Managing Vascular Dementia
While there is no cure for vascular dementia, several strategies can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Regular Exercise: Improves blood flow and supports mental health.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can support brain health.
- Smoking Cessation: Reducing the risk of blood vessel deterioration.
- Managing Stress: Relaxation activities like yoga and meditation.
Medical Treatments
- Medications: May include drugs to manage blood pressure, cholesterol, or to help improve memory.
- Therapies: Cognitive therapy or rehabilitation may be advised to support day-to-day functioning.
Supporting a Loved One with Vascular Dementia
As a caregiver, understanding your role and the steps to support someone with vascular dementia is crucial. Emotional and practical support can greatly affect the well-being of your loved one.
Tips for Caregivers
- Education: Understand the condition to provide informed support.
- Establish Routines: Familiar routines can reduce confusion and anxiety.
- Encourage Social Engagement: Keeps the mind active and spirits high.
- Practice Patience: Know that mood swings and frustration stem from the condition.
Practical Takeaways
- 🕒 Create a calming environment: Eliminate distractions and noise.
- 🧩 Encourage participation in simple activities: Keep the mind and body active.
- 💬 Maintain open communication: Listen compassionately.
- 📅 Use visual aids: Calendars or charts to keep track of routines.
Future Directions in Vascular Dementia Research
Research into vascular dementia continues to evolve, seeking to uncover more about its causes and develop better treatment options. Efforts are being made towards understanding genetic factors, identifying biomarkers, and exploring new therapeutic methods.
Emerging Trends
- Genetic Research: Understanding hereditary links.
- Advanced Imaging Techniques: To better track and understand brain changes.
- New Drug Trials: Investigations into medications that might slow progression.
Conclusion: Navigating Life with Vascular Dementia
Vascular dementia is a challenging condition, but understanding its facets allows for better management and improved quality of life for those affected. By staying informed and proactive, individuals and caregivers can navigate the complexities of this disease more effectively.
Care and management strategies, combined with advances in research, offer hope and avenues for maintaining mental acuity and life satisfaction despite the challenges posed by vascular dementia. Remember, support, patience, and informed actions form the crux of living well with this condition.
Understanding vascular dementia comprehensively equips you to face the condition more effectively, whether you're directly impacted or supporting a loved one. This journey involves continuous learning and adapting, ensuring that despite the hurdles, the journey remains as enriching as possible.
What You Get:
Free Dementia FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about What Is Vascular Dementia Disease and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about What Is Vascular Dementia Disease topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Dementia FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- Are Dementia And Alzheimer's The Same Thing
- Are Dementia Patients Insulin Resistant
- Can a Dog Get Dementia
- Can a Np Diagnose Dementia
- Can a Nursing Facility Diagnose Dementia Patients In California
- Can a Person With Dementia Divorce Their Spouse In California
- Can a Stroke Cause Dementia
- Can Adhd Turn Into Dementia
- Can Alcohol Abuse Cause Dementia
- Can Alcohol Cause Dementia
