Your Guide to How To Diagnose Dementia
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Dementia FAQ and related How To Diagnose Dementia topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about How To Diagnose Dementia topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Dementia FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
How Can You Identify Dementia? A Comprehensive Guide
The prospect of dementia is a concern for many, particularly as loved ones age. Understanding how to identify potential signs of dementia is crucial for early intervention and management. This guide delves into the nuances of diagnosing dementia, offering an insightful overview of the processes involved while underscoring the importance of professional evaluation.
Grasping the Fundamentals of Dementia
Dementia is not a single disease but a broad term that encompasses various conditions characterized by cognitive decline. Let's uncover what that means:
What Is Dementia?
Dementia is characterized by a decline in memory, problem-solving, and other cognitive abilities severe enough to impede daily life. Different stages and forms exist, making it critical to understand the specific type impacting an individual.
Common Types of Dementia
- Alzheimer’s Disease: The most common type, characterized by problems with memory, language, and thought processing.
- Vascular Dementia: Often arising after a stroke, it involves impaired judgment and information processing.
- Lewy Body Dementia: This form includes symptoms like hallucinations and difficulty with movement.
- Frontotemporal Dementia: Affects personality and behavior changes more than memory.
Understanding these types aids in recognizing symptoms that align specifically with different forms of dementia.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Awareness of early signs and symptoms can prompt timely consultation with healthcare providers. Here's a look at the hallmark indicators:
Early Warning Signs
- Memory Loss: Forgetting recent experiences or asking the same questions repeatedly.
- Language Problems: Difficulty finding the right words, leading to communication breakdowns.
- Disorientation: Getting lost in familiar places and losing track of time.
- Difficulty with Complex Tasks: Trouble planning, organizing, or concentrating.
Emotional and Behavioral Changes
- Mood Swings: Sudden or unexplained shifts in mood and personality.
- Apathy and Withdrawal: Loss of interest in activities once enjoyed.
- Social Challenges: Difficulty engaging in social settings due to memory or reasoning issues.
Professional Evaluation: Assessing Dementia
Once symptoms are noticed, professional evaluation is the next step. A comprehensive assessment involves several stages:
Initial Consultation
A primary care physician often spearheads the initial stage, referring patients to specialists if necessary. Information on the patient's history, daily functioning, and symptomatology is collected.
Cognitive and Functional Testing
Healthcare providers use a variety of tests to measure cognitive ability:
- Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE): A common test to assess memory, attention, and simple problem-solving abilities.
- Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA): Evaluates a broader range of cognitive functions including memory, attention, and visuospatial skills.
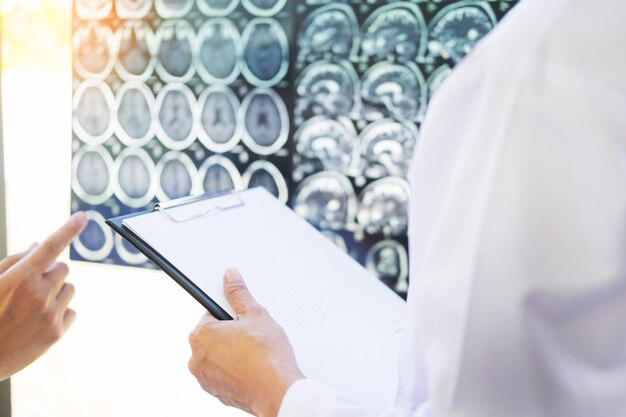
Neuroimaging and Laboratory Tests
Tests such as MRI or CT scans provide insight into brain structure, helping rule out conditions such as tumors or stroke. Blood tests can identify other factors that might mimic dementia symptoms, including hormonal imbalances or vitamin deficiencies.
Understanding the Role of Genetics and Risk Factors
Genetic factors and lifestyle choices play roles in dementia risk:
Genetic Predisposition
Some forms of dementia have a genetic component, particularly early-onset Alzheimer’s Disease. Genetic counseling can be beneficial for understanding risks in families with a history of dementia.
Modifiable Risk Factors
- Cardiovascular Health: High blood pressure or cholesterol can increase the risk.
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, alcohol use, and lack of physical activity can heighten the likelihood of developing dementia.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early diagnosis is crucial for several reasons:
- Treatment Options: While dementia can't be cured, early detection allows for more effective management of symptoms and planning for future care.
- Care Planning: Families can communicate preferences and make informed decisions prior to the disease’s progression.
- Support Systems: Early involvement in support groups can provide emotional and practical assistance.
Next Steps and Ongoing Management
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, several approaches can be taken:
Medical Interventions
There are medications available that aim to alleviate symptoms or slow progression. A healthcare provider can tailor these to meet individual needs.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Cognitive Stimulation: Engaging in puzzles and memory games can support cognitive function.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise aids overall health and can improve mental well-being.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet can support brain health. Omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins are beneficial.
Creating a Supportive Environment
Adapting living spaces to enhance safety and comfort is an ongoing process. Consider these tips:
- Simplifying Navigation: Clear labels and distinct color coding can help reduce confusion.
- Enhancing Safety: Install grab bars and remove tripping hazards.
- Promoting Independence: Encourage participation in daily activities with necessary adjustments.
Key Takeaways: Identifying and Managing Dementia
☑️ Prompt Evaluation: Seek professional advice if dementia symptoms are suspected.
☑️ Comprehensive Testing: Involves cognitive tests and medical imaging to distinguish from other conditions.
☑️ Risk Management: Addressing cardiovascular health and lifestyle changes can potentially reduce risk.
☑️ Symptom Management: Medications and lifestyle adjustments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
☑️ Support Systems: Establishing strong care networks and support systems is vital for patient and family well-being.
Dementia diagnosis is a complex process requiring medical evaluation to differentiate from other treatable conditions. Being informed about potential symptoms, types of dementia, and steps of professional assessment empowers individuals and families to take proactive and informed actions. By understanding these aspects, families can better navigate the path from diagnosis to effective management and care.
What You Get:
Free Dementia FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about How To Diagnose Dementia and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about How To Diagnose Dementia topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Dementia FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- Are Dementia And Alzheimer's The Same Thing
- Are Dementia Patients Insulin Resistant
- Can a Dog Get Dementia
- Can a Np Diagnose Dementia
- Can a Nursing Facility Diagnose Dementia Patients In California
- Can a Person With Dementia Divorce Their Spouse In California
- Can a Stroke Cause Dementia
- Can Adhd Turn Into Dementia
- Can Alcohol Abuse Cause Dementia
- Can Alcohol Cause Dementia
