Your Guide to How Is a Ct Different For a Dementia Patient
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Dementia FAQ and related How Is a Ct Different For a Dementia Patient topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about How Is a Ct Different For a Dementia Patient topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Dementia FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Understanding CT Scans for Dementia Patients: What You Need to Know
Imagine walking through a dense forest, trying to find your way with just a map. For many healthcare professionals diagnosing dementia, a CT scan serves as that map, providing a detailed internal view to help guide clinical decision-making. Today, we delve deep into how CT scans differ for dementia patients and why they are a crucial tool in diagnosing and managing this complex condition.
🧠 What is a CT Scan?
A Computed Tomography (CT) scan is a sophisticated imaging tool that combines X-ray measurements from different angles to generate cross-sectional images of the brain. These scans deliver detailed insights into the brain's structure, enabling physicians to identify any abnormalities that might suggest dementia.
Key Features of CT Scans
- Comprehensive Imaging: Provides detailed cross-sectional images, often referred to as slices, of the brain.
- Quick and Non-Invasive: Typically completed in minutes and does not require any incision.
- Detailed Visualization: Highlights bleeding, tumors, or bruising that may affect cognitive functions.
🔍 How CT Scans Aid in Dementia Diagnosis
CT scans are not a standalone diagnostic tool for dementia but serve an important role alongside clinical evaluations and other tests.
Differentiating Types of Dementia
CT scans help differentiate types of dementia by revealing characteristic structural changes. For example:
- Alzheimer's Disease: May reveal brain shrinkage particularly in the hippocampus.
- Vascular Dementia: Can show changes linked to blood vessel issues, such as strokes or blockages.
- Frontotemporal Dementia: May highlight atrophy in specific brain areas affecting behavior and language.
Spotting Other Conditions
CT scans can also detect other conditions that mimic dementia symptoms, such as:
- Tumors
- Hydrocephalus
- Subdural Hematomas
🩺 CT Scans vs. MRI for Dementia: What’s the Difference?
Both CT and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scans provide brain imaging but differ in their approach and applications in dementia cases.
CT Scan Advantages
- Speed and Accessibility: CT scans are typically faster and more widely available.
- Emergency Use: Ideal for initial assessments, especially in emergency settings.
MRI Advantages
- More Detail: Provides a more detailed view, especially of soft tissues.
- Greater Specificity: Better for fine details in suspecting specific dementia types.
Deciding Factors
The choice between a CT scan and an MRI may depend on:
- Clinical Indication: Immediate needs for information during emergencies.
- Availability: MRI machines may not be as readily accessible in all healthcare settings.
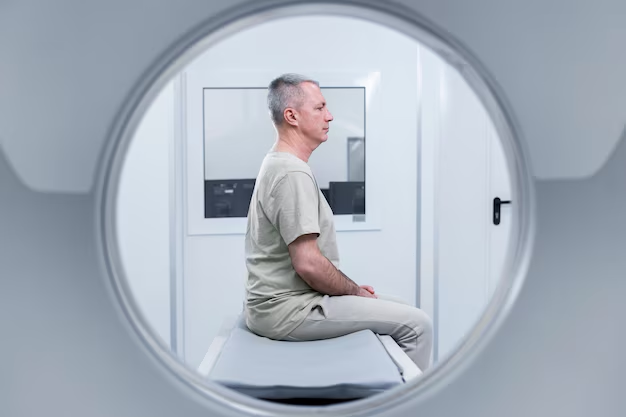
🛠️ Preparation and Procedure: What to Expect
For patients and caregivers, understanding what to expect can help manage anxiety associated with undergoing a CT scan.
Preparing for the Scan
- No Special Preparations: Generally, no restrictions on eating or drinking.
- Clothing: Patients might be asked to wear a hospital gown.
During the Procedure
- Duration: Typically takes only a few minutes.
- Positioning: The patient will lie on a table that slides into the scanner.
- Sensations: Usually painless; however, some may experience brief anxiety due to the enclosed space.
🧩 Safety Considerations for Dementia Patients
Safety is a primary concern, especially for patients with dementia who might experience confusion or anxiety during medical procedures.
Key Safety Practices
- Communication: Clear explanations before and during the scan help alleviate fear.
- Companionship: Allowing a caregiver or familiar person in the room may comfort the patient.
- Minimal Restraint: Gentle encouragement and minimal physical restraint promote cooperation.
Addressing Anxiety
Healthcare providers might recommend techniques or mild sedation in cases of extreme anxiety, always ensuring the patient's comfort and safety are prioritized.
💡 How CT Scans Inform Treatment Plans
Once the CT scan results are available, they guide the next steps in a patient’s care journey.
Comprehensive Care Planning
- Multi-Disciplinary Approach: Incorporates input from neurologists, psychiatrists, and other specialists.
- Personalized Treatment: Tailors interventions based on the specific type and progression of dementia.
Monitoring Progression
Regular CT scans may help monitor the brain's structural changes over time, providing insights into the effectiveness of treatments.
📋 Quick Summary: CT Scans for Dementia Patients
Here’s a handy overview of the key takeaways from this discussion about CT scans and dementia:
- Purpose: Diagnostic tool providing detailed images of the brain.
- Types of Dementia Differentiation: Effective in identifying structural changes related to different dementia types.
- Safety: Non-invasive, with minimal risk, especially when precautions are taken to manage anxiety.
- Complementary Tool: Works alongside other diagnostic measures for a holistic understanding of a patient's condition.
Why It Matters
Understanding these aspects empowers patients and caregivers to take an active role in the decision-making process regarding dementia diagnosis and management.
In the world of dementia diagnosis, CT scans are a powerful tool. They provide the clarity needed to navigate the complex terrain of brain health and enable healthcare professionals to devise informed, patient-centric treatment strategies. As advancements in imaging technology continue, the role of CT scans in managing dementia is bound to grow, offering hope and understanding in the face of one of the most challenging health issues of our time.
What You Get:
Free Dementia FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about How Is a Ct Different For a Dementia Patient and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about How Is a Ct Different For a Dementia Patient topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Dementia FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- Are Dementia And Alzheimer's The Same Thing
- Are Dementia Patients Insulin Resistant
- Can a Dog Get Dementia
- Can a Np Diagnose Dementia
- Can a Nursing Facility Diagnose Dementia Patients In California
- Can a Person With Dementia Divorce Their Spouse In California
- Can a Stroke Cause Dementia
- Can Adhd Turn Into Dementia
- Can Alcohol Abuse Cause Dementia
- Can Alcohol Cause Dementia
