Your Guide to Are Cataracts Hereditary
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Cataract FAQ and related Are Cataracts Hereditary topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about Are Cataracts Hereditary topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Cataract FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Are Cataracts Passed Down Through Families? Exploring the Hereditary Nature of This Common Eye Condition
Have you ever wondered if your vision problems are due to your family history? When it comes to cataracts, a common eye condition that clouds the lens of the eye, many people are curious about whether they might have inherited it from their parents or grandparents. In this article, we'll dive into the world of cataracts, exploring their hereditary nature, other potential risk factors, and what you can do to manage or even prevent them.
What Are Cataracts and How Do They Form?
Understanding Cataracts
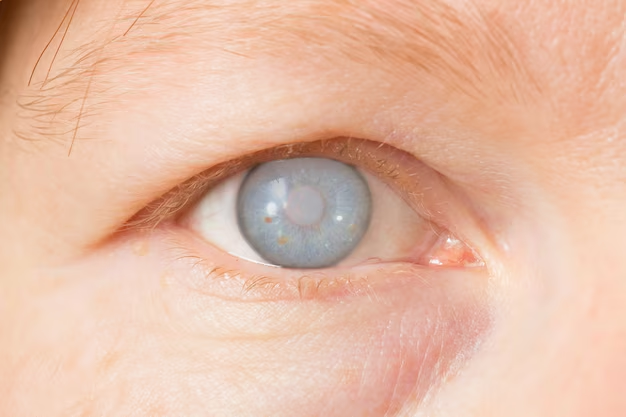
A cataract is a clouding of the lens in your eye, which leads to a decrease in vision. This condition typically develops slowly and can affect one or both eyes. As the cataract matures, it can interfere with light passing through the lens to the retina, resulting in blurred or dimmed vision.
How Cataracts Develop
The formation of cataracts is a gradual process. The lens of your eye is primarily made up of water and proteins. With age or due to other factors, these proteins can clump together, creating a cloudy area on the lens. Over time, this can enlarge, making it increasingly difficult to see clearly.
Are Cataracts Hereditary?
The Role of Genetics in Cataracts
Genetics can indeed play a role in the development of cataracts. Some studies and expert perspectives suggest that if your family has a history of cataracts, you might have an increased risk of developing them. However, this genetic predisposition is just one piece of the puzzle.
- Congenital cataracts, for example, are present at birth and can be hereditary.
- Age-related cataracts, the most common type, can also have a genetic component.
Other Risk Factors
While genetics can contribute to cataract formation, it's not the sole factor. Here are other common risk factors:
- Age: Most cataracts are age-related, with the majority occurring in those over 60.
- Exposure to sunlight: Ultraviolet radiation from the sun can increase the risk.
- Health conditions: Chronic diseases such as diabetes are known contributors.
- Lifestyle choices: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can elevate risk levels.
How Can You Identify Cataracts Early?
Symptoms to Watch For
Cataracts often develop slowly and painlessly, which can make them difficult to detect without regular eye exams. However, there are some symptoms to look out for:
- Blurry or cloudy vision
- Increased sensitivity to light and glare
- Seeing "halos" around lights
- Fading or yellowing of colors
- Frequent prescription changes in eyewear
Routine Eye Exams
Regular eye examinations are crucial for early detection. Eye doctors can identify cataracts before symptoms become apparent, offering a better chance of managing the condition effectively.
Managing Cataracts: What Are Your Options?
Non-Surgical Management
In the early stages, cataracts might not significantly impact your vision. Here are some ways to cope with mild symptoms:
- Use brighter lighting at home or work.
- Wear anti-glare sunglasses to reduce light sensitivity.
- Update your eyeglass prescription for better clarity.
Surgical Intervention
When cataracts begin to impede your daily activities, surgery may be recommended. Cataract surgery is a common and generally safe procedure where the cloudy lens is replaced with a clear artificial one. Most people experience significant improvements in vision afterward.
Preparing for Surgery
If you opt for cataract surgery, here's how you can prepare:
- Discuss your medical history with your eye surgeon.
- Plan for post-operative care and arrange transportation as you'll need assistance immediately after the procedure.
- Follow any pre-surgery instructions provided by your healthcare, including fasting or medication adjustments.
Lifestyle Adjustments to Lower Your Cataract Risk
Diet and Nutrition
Adopting a diet rich in antioxidants can support eye health. Here's how you can adjust your nutrition:
- Increase intake of vitamins C and E, found in fruits and vegetables.
- Incorporate omega-3 fatty acids from fish like salmon or flaxseeds.
- Consume lutein and zeaxanthin, nutrients present in leafy greens like spinach and kale.
Protecting Your Eyes
To reduce exposure to potential cataract causes, consider these protective measures:
- Wear sunglasses with UV protection when outdoors.
- Use wide-brimmed hats to shield your eyes from direct sunlight.
- Limit screen time or use blue light filters, since excessive screen exposure can strain your eyes.
A Practical Guide: Lifestyle Changes to Support Eye Health
Here’s a simple breakdown of steps you can take to mitigate cataract risk:
| Step | Action | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 🥦 | Prioritize a balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 rich foods | Supports overall eye health |
| 🎓 | Educate yourself on your family history of eye conditions | Awareness leads to proactive health checks |
| 😎 | Wear sunglasses and hats | Reduces ultraviolet exposure |
| 💧 | Stay hydrated | Maintains overall body health, including eye health |
| 🚭 | Avoid smoking | Lowers chance of cataract development |
The Importance of Genetic Counseling
Understanding Your Family History
With genetics playing a part in the risk factor for cataracts, genetic counseling can help you better understand your risk and provide insight into how hereditary factors might affect you.
When to Consider Genetic Counseling
- If cataracts develop at a young age within your family.
- If you or someone in your family is diagnosed with congenital cataracts.
- If you have questions regarding other hereditary eye conditions.
The Takeaway: Is Family History Everything?
While your family history can influence your risk of developing cataracts, it’s just one element in a broader spectrum of factors. Understanding your genetic predisposition can empower you to make informed decisions about eye care and lifestyle changes.
By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, protecting your eyes, and keeping up with regular eye examinations, you can take significant steps towards preserving your vision well into your later years. Remember, your vision is invaluable—take proactive measures to care for it!
In summary, cataracts can be hereditary, but they are also influenced by age, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Knowing how these elements interplay allows for a proactive approach to managing and potentially preventing vision issues. Always consult with professionals for personalized guidance and make informed decisions regarding your eye health. 👁️✨
What You Get:
Free Cataract FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about Are Cataracts Hereditary and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about Are Cataracts Hereditary topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Cataract FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.