Your Guide to Is There a Test For Rheumatoid Arthritis
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Arthritis FAQ and related Is There a Test For Rheumatoid Arthritis topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about Is There a Test For Rheumatoid Arthritis topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Arthritis FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Discovering Rheumatoid Arthritis: Is There a Test?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can be a formidable disease, presenting both challenges in diagnosis and in managing symptoms. If you've found yourself asking, "Is there a test for rheumatoid arthritis?" you're not alone. This question highlights not only the complexity of RA but also the desire for clarity in understanding one's health. In this guide, we'll explore the intricacies of diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis, delving into the available tests, related conditions, and what it all means for those potentially affected by this chronic illness.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition characterized by inflammation of the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and sometimes joint deformity. Unlike osteoarthritis, which results from wear and tear, RA involves the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy joint tissues. This distinction is crucial as it influences symptoms, disease progression, and treatment approaches.
Symptoms to Watch Out For
Recognizing symptoms early can lead to faster diagnosis and management:
- Persistent joint pain
- Swelling and tenderness in the joints
- Morning stiffness lasting longer than an hour
- Fatigue and fever
- Loss of joint function and deformities over time
Each person's experience with RA can vary significantly, emphasizing the importance of tailored medical evaluations and interventions.
The Path to Diagnosis
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis is a multifaceted process. There isn't a single test that confirms RA, making it essential to combine clinical evaluations with various testing methods.
Clinical Examination
A healthcare provider typically starts with a detailed medical history and a physical examination to assess joint inflammation and tenderness. This step helps rule out other conditions and provides context for further testing.
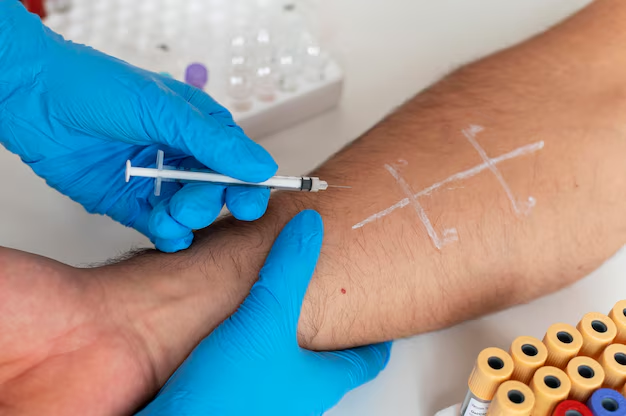
Laboratory Tests
Several blood tests aid in RA diagnosis:
Rheumatoid Factor (RF) Test: RF is an antibody found in higher levels among many RA patients. However, its presence alone isn't definitive, as it can also be found in other diseases or even in healthy individuals.
Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (Anti-CCP) Test: More specific than RF, anti-CCP antibodies often indicate RA, especially in those with early-stage symptoms.
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) and C-Reactive Protein (CRP): These tests measure inflammation levels within the body. While elevated levels are common in RA, they aren't exclusive to the disease.
Imaging Studies
X-rays and Ultrasounds: These imaging tools help visualize joint erosion and swelling. Regular monitoring can illustrate disease progression or treatment efficacy.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI offers a more detailed look at joint and tissue abnormalities, making it especially useful in early RA detection.
Differential Diagnosis
RA shares symptoms with other conditions, so pinpointing the exact ailment requires ruling out similar diseases such as:
- Osteoarthritis
- Lupus
- Gout
Monitoring RA: Beyond Diagnosis
Once diagnosed, ongoing monitoring is crucial for managing RA efficiently. This involves a combination of regular doctor visits, symptom tracking, and potentially adjusting treatment plans as needed.
Disease Activity Scores
Disease Activity Scores (DAS), like DAS28 which measures tender and swollen joints, offer a quantifiable method to monitor RA's impact. These evaluations help in making informed adjustments to treatment protocols.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
The earlier RA is diagnosed, the more effective treatments can be. Early intervention is linked to better long-term outcomes, potentially reducing the risk of joint damage and improving quality of life.
Empowering Your Health Journey
Lifestyle Modifications
While living with RA poses challenges, several lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and improve overall wellbeing:
- Exercise: Regular, low-impact activities like walking or swimming can boost joint mobility and reduce stiffness.
- Diet: An anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, and vegetables can be beneficial.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can alleviate stress, which might exacerbate symptoms.
When to Consult a Specialist
If you suspect RA or experience persistent joint issues, consulting a rheumatologist—an arthritis specialist—can provide tailored advice and treatment options.
Collaborative Care
RA management often involves a healthcare team. Beyond rheumatologists, this may include physical therapists, nutritionists, and pharmacists, all working together to offer comprehensive care.
Key Takeaways: Navigating Your RA Journey
Here are some critical points to remember about rheumatoid arthritis:
- 🔍 Symptoms: Persistent joint pain, morning stiffness, and swelling are red flags for RA.
- 🩺 Tests: No single test diagnoses RA; a combination of blood tests, imaging, and clinical evaluations is necessary.
- 📈 Monitoring: Regular check-ups and disease activity scores are vital in tracking and managing RA effectively.
- 🥗 Lifestyle: Incorporate regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management techniques.
- 🤝 Specialists: Early consultation with a rheumatologist can significantly benefit treatment outcomes.
Navigating a Complex Disease with Confidence
Although finding a test for rheumatoid arthritis can seem daunting, understanding the comprehensive approach to diagnosing and managing the condition can demystify the process. By recognizing symptoms early, seeking appropriate medical guidance, and actively participating in your health journey, it's possible to navigate the challenges of RA with confidence. Remember, you're not alone—leveraging available resources and professional support can make a significant difference in living well with rheumatoid arthritis.
What You Get:
Free Arthritis FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about Is There a Test For Rheumatoid Arthritis and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about Is There a Test For Rheumatoid Arthritis topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Arthritis FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Septic Arthritis
- Are Bananas Bad For Arthritis
- Are Tomatoes Bad For Arthritis
- Can An Inflamed Nerve Cause Arthritis
- Can An Inflamed Nerve Cause Arthritis In Dogs
- Can An x Ray Show Arthritis
- Can Arthritis Be Cured
- Can Arthritis Be Reversed
- Can Arthritis Become Septic After Infection From Injection
- Can Arthritis Cause Numbness
