Your Guide to How To Know If You Have Arthritis
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Arthritis FAQ and related How To Know If You Have Arthritis topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about How To Know If You Have Arthritis topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Arthritis FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
Is it Arthritis? A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Your Symptoms
Few things can be more frustrating than persistent joint pain and stiffness. As these unwelcome sensations interfere with daily life, a lingering question may emerge: could this be arthritis? Understanding arthritis is essential for recognizing the symptoms and considering potential next steps. By learning about the different types of arthritis, symptoms, and how it's typically diagnosed, you'll empower yourself with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions.
Understanding Arthritis: An Overview
Arthritis isn’t a single disease but a broad term encompassing over 100 different conditions that affect the joints. While symptoms vary, joint pain, swelling, and stiffness are common across most types. Arthritis can affect individuals of all ages, but it’s often associated with older adults.
What Is Arthritis?
At its core, arthritis means inflammation of the joints. This inflammation can lead to symptoms like pain, swelling, and reduced motion. There are two prevalent forms of arthritis:
Osteoarthritis (OA): Often called "wear and tear" arthritis, OA involves the gradual erosion of cartilage — the smooth, protective tissue at the ends of bones that enables painless joint motion. This degeneration leads to pain and stiffness, usually in the hands, knees, hips, or spine.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Unlike OA, which is primarily a mechanical issue, RA is an autoimmune condition. The immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium — the lining of the joints — leading to inflammation and joint damage.
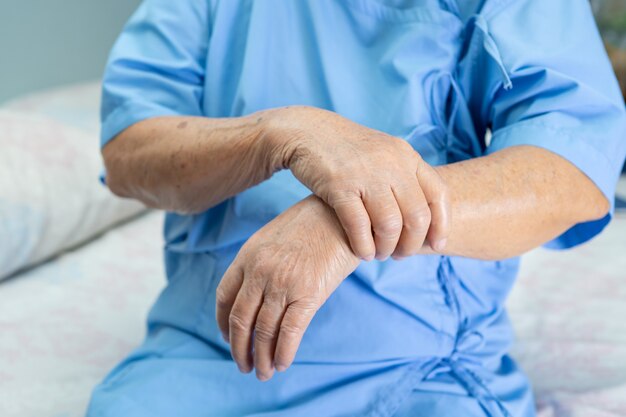
Signs and Symptoms of Arthritis
Recognizing the symptoms of arthritis is a critical first step. While each type of arthritis may manifest differently, certain signs often serve as red flags.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
- Joint Pain: A persistent ache in a specific joint or multiple joints is a hallmark symptom.
- Swelling: Inflammation can cause visible swelling around affected joints.
- Stiffness: Many people with arthritis experience stiffness, particularly in the morning or after prolonged rest.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Joints may lose flexibility, leading to difficulty in movement.
- Redness and Warmth: An affected joint may appear red and feel warm to the touch.
💡 Tip: If these symptoms are recurrent or worsening, it might be time to seek medical advice.
Distinguishing Features of Osteoarthritis vs. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Understanding the nuances between OA and RA can help indicate which type you might be experiencing.
- Osteoarthritis: Symptoms often worsen with activity and improve with rest. Joints may appear larger, and people often report a creaking sensation.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms are usually symmetrical, affecting the same joints on both sides of the body. RA often causes systemic symptoms such as fatigue and fever.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While self-monitoring for arthritis symptoms is beneficial, knowing when to consult a healthcare professional is crucial.
Indicators to Consult a Doctor
- Persistent or Worsening Pain: If joint pain does not improve with conservative measures like rest and over-the-counter pain relievers, medical advice may be needed.
- Sudden Swelling or Redness: These can indicate an acute inflammatory process requiring prompt attention.
- Symptoms Affect Daily Function: When arthritis affects your ability to perform routine tasks, professional evaluation is warranted.
How Arthritis Is Diagnosed
If you suspect you have arthritis, your healthcare provider will follow a systematic approach to diagnose the condition.
Initial Evaluation and Tests
- Medical History: A detailed account of your symptom history, lifestyle, and any family history of arthritis.
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of affected joints for signs like warmth, swelling, and tenderness.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds may be used to assess joint degeneration or inflammation.
- Lab Tests: Blood tests can check for inflammatory markers and antibodies commonly associated with RA.
What to Expect at Your Appointment
An appointment with a healthcare provider for arthritis concerns typically involves discussing your symptoms, physical examination, and possibly scheduling tests to confirm a diagnosis. It's helpful to prepare a list of symptoms and consider any potential triggers to share during your visit.
Lifestyle Changes and Management
While medial diagnosis is key to managing arthritis, certain lifestyle changes can help minimize symptoms and maintain joint health.
Managing Arthritis with Diet and Exercise
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Extra weight adds stress to joints, especially those in the lower body. Weight management can alleviate pressure and reduce pain.
- Regular Exercise: Low-impact activities, such as walking, swimming, and cycling, can enhance flexibility and strengthen muscles around joints.
- Balanced Diet: Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory properties — like fish, berries, and leafy greens — might have beneficial effects.
Protecting Your Joints
- Use Assistive Devices: Items like canes or braces can support joints and reduce strain.
- Practice Good Posture: Maintaining proper posture minimizes unnecessary joint stress.
- Avoid Repetitive Motions: When possible, vary tasks to prevent overuse of specific joints.
Various Types of Arthritis
While OA and RA are the most common, you might encounter other types:
- Psoriatic Arthritis: Associated with psoriasis, causing joint pain and skin symptoms.
- Gout: Caused by uric acid crystals in joints, leading to sudden, severe pain — often in the big toe.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: Affects the spine, leading to pain and stiffness, particularly in the lower back and pelvis.
Practical Summary and Tips
Here's a concise guide to help navigate the world of arthritis:
- 📝 Symptom Tracking: Keep a diary of symptom frequency, severity, and triggers.
- 🏋️♀️ Activity Adjustment: Engage in low-impact exercises to keep joints flexible.
- 🍽️ Nutritional Focus: Adopt a diet with anti-inflammatory foods.
- 🤝 Seek Support: Join arthritis support groups to share experiences and coping strategies.
Empowering yourself with knowledge and taking proactive steps can lead to better joint health and improved quality of life. Remember, the journey with arthritis is unique for everyone, and early attention to symptoms can make a significant difference in management and comfort.
What You Get:
Free Arthritis FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about How To Know If You Have Arthritis and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about How To Know If You Have Arthritis topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Arthritis FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Septic Arthritis
- Are Bananas Bad For Arthritis
- Are Tomatoes Bad For Arthritis
- Can An Inflamed Nerve Cause Arthritis
- Can An Inflamed Nerve Cause Arthritis In Dogs
- Can An x Ray Show Arthritis
- Can Arthritis Be Cured
- Can Arthritis Be Reversed
- Can Arthritis Become Septic After Infection From Injection
- Can Arthritis Cause Numbness
