Your Guide to How Does Arthritis Begin
What You Get:
Free Guide
Free, helpful information about Arthritis FAQ and related How Does Arthritis Begin topics.
Helpful Information
Get clear and easy-to-understand details about How Does Arthritis Begin topics and resources.
Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to receive offers or information related to Arthritis FAQ. The survey is optional and not required to access your free guide.
How Does Arthritis Develop? Understanding the Onset of Joint Pain
Arthritis is a common ailment that affects millions, causing pain and limiting mobility. But how does arthritis actually begin? Understanding the roots of this condition is not only crucial for those at risk but also enlightening for anyone seeking to understand the mechanics of joint health. In this guide, we'll explore how arthritis starts, delve into related subtopics, and provide you with engaging insights to make sense of this complex condition.
🌟 The Early Mechanisms of Arthritis
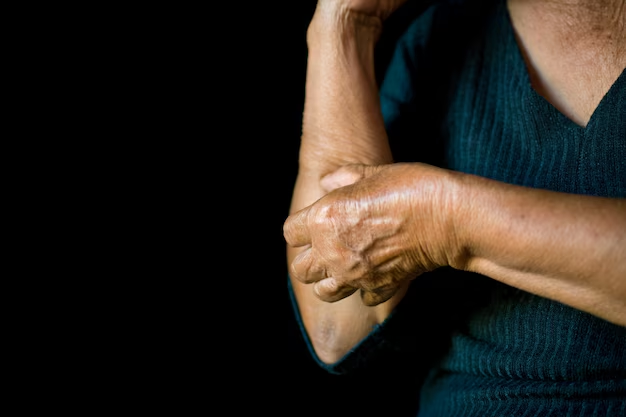
Arthritis doesn't develop overnight. It often begins subtly, with mild symptoms that gradually escalate. Generally, it starts with deterioration at the cellular level within joint tissues. The term "arthritis" encompasses various types that affect the body differently, but most forms share common early signs and triggers.
🧬 The Role of Genetics and Lifestyle
Many factors blend to determine how and when arthritis begins. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, meaning if your family has a history of arthritis, your chances of developing it are higher. Lifestyle factors, such as obesity, diet, and physical activity level, also significantly influence when and how arthritis might manifest.
- Genetic Factors influence the likelihood of developing specific types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, which is an autoimmune condition.
- Lifestyle Choices, including maintaining a healthy weight and regular exercise, can delay or prevent the onset of some arthritis forms.
🏋️♀️ Wear and Tear: Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is often called the "wear and tear" arthritis due to its nature. It occurs when cartilage, the cushion between bones, wears down over time. This can result from repetitive joint use, making athletes and those in physically demanding jobs more susceptible.
- Early Symptoms: Stiffness and minor pain during or after movement.
- Progression: Over time, bones in the joint may start to rub directly against each other, leading to significant pain and reduced mobility.
🤕 Inflammatory Origins: Rheumatoid Arthritis
On the other side of the spectrum is Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks joint tissues, causing inflammation.
Common Early Signs of RA include:
- Morning stiffness lasting longer than an hour.
- Joint swelling and tenderness.
- Fatigue and mild fever.
Understanding these initial symptoms can prompt early consultation with healthcare providers, potentially improving management outcomes.
🔎 Deeper Dive: Factors That Trigger Arthritis
Understanding how arthritis starts also involves exploring what triggers it. Various factors beyond genetics and use patterns can spark joint deterioration.
⚖️ Hormonal Influences
Hormones can significantly impact arthritis risk, particularly in women. Estrogen levels fluctuate throughout life — during pregnancy and menopause — and can affect joint health and arthritis onset.
- Some women may notice arthritis symptoms intensify during menopause, as estrogen levels decrease.
💡 Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors also come into play. Exposure to toxins, such as tobacco smoke, can enhance inflammation, hastening arthritis’s onset and progression.
- Smoking is strongly linked to increased RA risk, while certain occupational exposures might influence OA development.
🌱 The Intersection of Age and Arthritis
Age is a well-known factor in arthritis development, with many associating the condition with older adults. However, arthritis can start at any age.
👶 Juvenile Arthritis
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) is a condition that affects children and adolescents. This form of arthritis presents unique challenges, emphasizing the importance of early recognition and management to safeguard young individuals' quality of life.
👵 Aging and Arthritis
With time, the body's ability to repair and maintain joint tissues diminishes. As people age, they naturally face an increased risk of osteoarthritis and other degenerative joint conditions.
- Preventive measures, such as maintaining joint health through diet and exercise, become increasingly important with age.
🏃♂️ What Can You Do?
Understanding how arthritis starts empowers you to take proactive steps toward joint health. While we can't entirely prevent the condition, certain strategies can help manage risks and alleviate symptoms.
🔍 Monitor Regularly
Regular check-ups and being attuned to your body's signals can help catch early signs of arthritis. This awareness can lead to timely interventions, potentially preventing severe progression.
🍴 Adopt a Joint-Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamin D can support joint health. Fatty fish, leafy greens, and nuts should feature prominently in your meals.
🏋️♂️ Stay Active
Incorporate exercises that enhance joint flexibility and muscle strength. Low-impact activities such as swimming, yoga, and cycling are ideal for maintaining joint health without excessive strain.
📝 Summary and Key Takeaways
Here's a bullet-point list highlighting key insights on arthritis onset:
- 🧬 Genetics and Lifestyle: Genetics and lifestyle choices significantly affect arthritis.
- 🤕 Identify Early Signs: Be aware of stiffness, swelling, and fatigue.
- ⚖️ Hormonal Effects: Women might notice changes around menopause.
- 🔍 Stay Vigilant: Routine medical check-ups are essential.
- 🏋️♂️ Exercise Regularly: Participating in joint-friendly activities is crucial.
- 🍴 Balanced Diet: Consume foods rich in omega-3s and antioxidants.
Understanding how arthritis begins allows you to make informed decisions for your joint health. By recognizing early signs and integrating preventive measures, you can potentially delay onset and improve your quality of life. Embrace these insights not just as pieces of information, but as powerful tools to guide your journey toward better health. 🌟
What You Get:
Free Arthritis FAQ Guide
Free, helpful information about How Does Arthritis Begin and related resources.

Helpful Information
Get clear, easy-to-understand details about How Does Arthritis Begin topics.

Optional Personalized Offers
Answer a few optional questions to see offers or information related to Arthritis FAQ. Participation is not required to get your free guide.

Discover More
- a Septic Arthritis
- Are Bananas Bad For Arthritis
- Are Tomatoes Bad For Arthritis
- Can An Inflamed Nerve Cause Arthritis
- Can An Inflamed Nerve Cause Arthritis In Dogs
- Can An x Ray Show Arthritis
- Can Arthritis Be Cured
- Can Arthritis Be Reversed
- Can Arthritis Become Septic After Infection From Injection
- Can Arthritis Cause Numbness
